Page 110 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 110
Combustion Technology 79
gases and descending cake provide contact between the hot combustion gases and
the cake feed solids to ensure complete combustion.
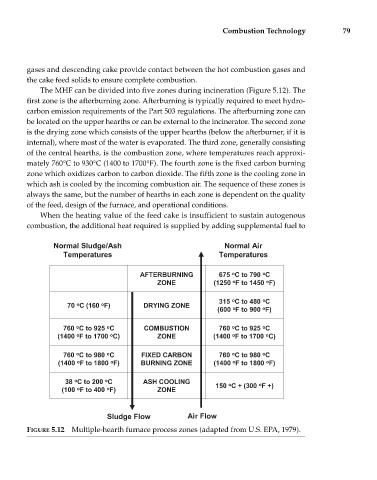
The MHF can be divided into five zones during incineration (Figure 5.12). The
first zone is the afterburning zone. Afterburning is typically required to meet hydro-
carbon emission requirements of the Part 503 regulations. The afterburning zone can
be located on the upper hearths or can be external to the incinerator. The second zone
is the drying zone which consists of the upper hearths (below the afterburner, if it is
internal), where most of the water is evaporated. The third zone, generally consisting
of the central hearths, is the combustion zone, where temperatures reach approxi-
mately 760°C to 930°C (1400 to 1700°F). The fourth zone is the fixed carbon burning
zone which oxidizes carbon to carbon dioxide. The fifth zone is the cooling zone in
which ash is cooled by the incoming combustion air. The sequence of these zones is
always the same, but the number of hearths in each zone is dependent on the quality
of the feed, design of the furnace, and operational conditions.
When the heating value of the feed cake is insufficient to sustain autogenous
combustion, the additional heat required is supplied by adding supplemental fuel to
FIGURE 5.12 Multiple-hearth furnace process zones (adapted from U.S. EPA, 1979).