Page 155 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 155
122 Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
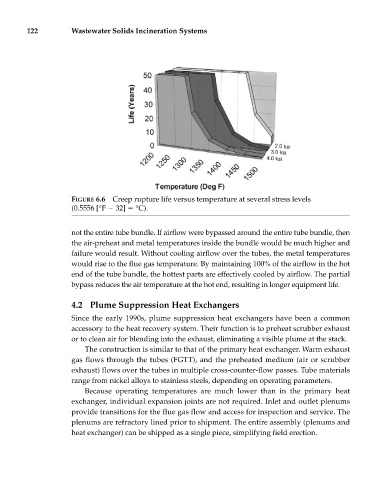
FIGURE 6.6 Creep rupture life versus temperature at several stress levels
(0.5556 [°F 32] °C).
not the entire tube bundle. If airflow were bypassed around the entire tube bundle, then
the air-preheat and metal temperatures inside the bundle would be much higher and
failure would result. Without cooling airflow over the tubes, the metal temperatures
would rise to the flue gas temperature. By maintaining 100% of the airflow in the hot
end of the tube bundle, the hottest parts are effectively cooled by airflow. The partial
bypass reduces the air temperature at the hot end, resulting in longer equipment life.
4.2 Plume Suppression Heat Exchangers
Since the early 1990s, plume suppression heat exchangers have been a common
accessory to the heat recovery system. Their function is to preheat scrubber exhaust
or to clean air for blending into the exhaust, eliminating a visible plume at the stack.
The construction is similar to that of the primary heat exchanger. Warm exhaust
gas flows through the tubes (FGTT), and the preheated medium (air or scrubber
exhaust) flows over the tubes in multiple cross-counter-flow passes. Tube materials
range from nickel alloys to stainless steels, depending on operating parameters.
Because operating temperatures are much lower than in the primary heat
exchanger, individual expansion joints are not required. Inlet and outlet plenums
provide transitions for the flue gas flow and access for inspection and service. The
plenums are refractory lined prior to shipment. The entire assembly (plenums and
heat exchanger) can be shipped as a single piece, simplifying field erection.