Page 80 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 80
Combustion Technology 49
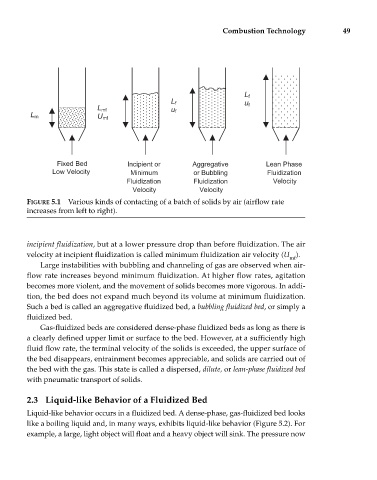
FIGURE 5.1 Various kinds of contacting of a batch of solids by air (airflow rate
increases from left to right).
incipient fluidization, but at a lower pressure drop than before fluidization. The air
velocity at incipient fluidization is called minimum fluidization air velocity (U ).
mf
Large instabilities with bubbling and channeling of gas are observed when air-
flow rate increases beyond minimum fluidization. At higher flow rates, agitation
becomes more violent, and the movement of solids becomes more vigorous. In addi-
tion, the bed does not expand much beyond its volume at minimum fluidization.
Such a bed is called an aggregative fluidized bed, a bubbling fluidized bed, or simply a
fluidized bed.
Gas-fluidized beds are considered dense-phase fluidized beds as long as there is
a clearly defined upper limit or surface to the bed. However, at a sufficiently high
fluid flow rate, the terminal velocity of the solids is exceeded, the upper surface of
the bed disappears, entrainment becomes appreciable, and solids are carried out of
the bed with the gas. This state is called a dispersed, dilute, or lean-phase fluidized bed
with pneumatic transport of solids.
2.3 Liquid-like Behavior of a Fluidized Bed
Liquid-like behavior occurs in a fluidized bed. A dense-phase, gas-fluidized bed looks
like a boiling liquid and, in many ways, exhibits liquid-like behavior (Figure 5.2). For
example, a large, light object will float and a heavy object will sink. The pressure now