Page 68 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 68
46
Water Sources: Groundwater
Chapter 3
Table 3.1
US water sources in 2007
Water system
Totals
a
40,646
52,095
Community water system
11,449
No. of systems
195,887,109
90,549,995
Population served
22
Percentage of systems
100
78
68
Percentage of population
100
32
b
18,830
18,151
No. of systems
679
Nontransient noncommunity water system
5,503,282
Population served
787,555
6,290,837
100
Percentage of systems
4
96
Percentage of population
13
87
100
c
82,851
84,729
1,878
Transient noncommunity water system
No. of systems
2,668,985
11,077,369
13,746,354
Population served Groundwater Surface water 286,437,104
Percentage of systems 98 2 100
Percentage of population 81 19 100
Total no. of systems 141,648 14,006 155,654
Source: Courtesy US Environmental Protection Agency.
a Community water system: a public water system that supplies water to the same population year-round.
b Nontransient noncommunity water system: a public water system that regularly supplies water to at least 25 of the same people at least 6 months per year,
but not year-round. Some examples are schools, factories, office buildings, and hospitals that have their own water systems.
c
Transient noncommunity water system: a public water system that provides water in a place such as a gas station or campground where people do not
remain for long periods of time.
place by molecular and surface tension forces. This is the effective porosity,or specific yield of the material, defined
dead storage and is called specific retention. Thus not all as the proportion of water in the pores that is free to drain
the water stored in a geologic formation can be withdrawn away or be withdrawn under the influence of gravity. Spe-
by normal engineering operations. Accordingly, there is a cific yields vary from 0 for plastic clays to 30% or more
difference between total storage and useful storage. That for uniform sands and gravels. Most aquifers have yields
portion of the pore space in which flow takes place is called of 10–20%.
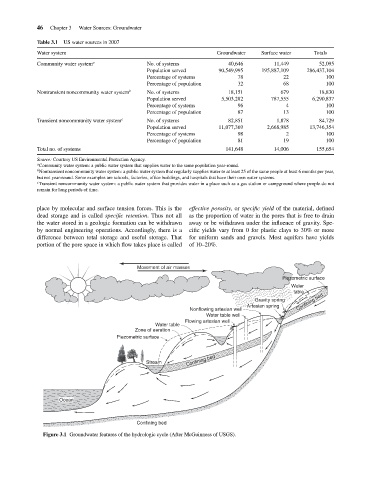
Movement of air masses
Piezometric surface
Water
table
Gravity spring Confining bed
Artesian spring
Nonflowing artesian well
Water table well
Flowing artesian well
Water table
Zone of aeration
Piezometric surface
Confining bed
Stream
Ocean
Confining bed
Figure 3.1 Groundwater features of the hydrologic cycle (After McGuinness of USGS).