Page 189 - Water Loss Control
P. 189
Contr olling Appar ent Losses—Capturing Missing Revenue and Data Integrity 163
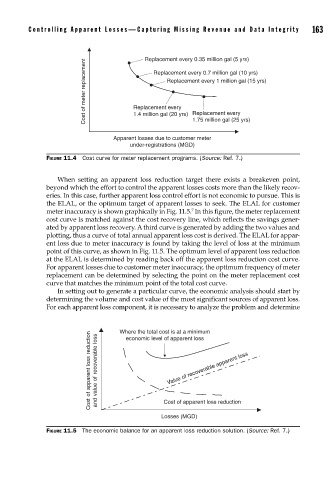
Replacement every 0.35 million gal (5 yrs)
Cost of meter replacement Replacement every
Replacement every 0.7 million gal (10 yrs)
Replacement every 1 million gal (15 yrs)
1.4 million gal (20 yrs) Replacement every
1.75 million gal (25 yrs)
Apparent losses due to customer meter
under-registrations (MGD)
FIGURE 11.4 Cost curve for meter replacement programs. (Source: Ref. 7.)
When setting an apparent loss reduction target there exists a breakeven point,
beyond which the effort to control the apparent losses costs more than the likely recov-
eries. In this case, further apparent loss control effort is not economic to pursue. This is
the ELAL, or the optimum target of apparent losses to seek. The ELAL for customer
7
meter inaccuracy is shown graphically in Fig. 11.5. In this figure, the meter replacement
cost curve is matched against the cost recovery line, which reflects the savings gener-
ated by apparent loss recovery. A third curve is generated by adding the two values and
plotting, thus a curve of total annual apparent loss cost is derived. The ELAL for appar-
ent loss due to meter inaccuracy is found by taking the level of loss at the minimum
point of this curve, as shown in Fig. 11.5. The optimum level of apparent loss reduction
at the ELAL is determined by reading back off the apparent loss reduction cost curve.
For apparent losses due to customer meter inaccuracy, the optimum frequency of meter
replacement can be determined by selecting the point on the meter replacement cost
curve that matches the minimum point of the total cost curve.
In setting out to generate a particular curve, the economic analysis should start by
determining the volume and cost value of the most significant sources of apparent loss.
For each apparent loss component, it is necessary to analyze the problem and determine
Cost of apparent loss reduction and value of recoverable loss Value of recoverable apparent loss
Where the total cost is at a minimum
economic level of apparent loss
Cost of apparent loss reduction
Losses (MGD)
FIGURE 11.5 The economic balance for an apparent loss reduction solution. (Source: Ref. 7.)