Page 327 - Water Loss Control
P. 327
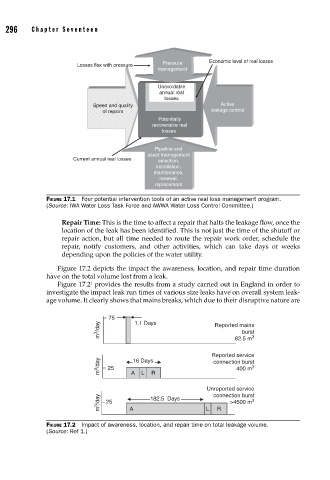
296 Cha pte r Se v e ntee n
Losses flex with pressure Pressure Economic level of real losses
management
Unavoidable
annual real
losses
Speed and quality Active
of repairs leakage control
Potentially
recoverable real
losses
Pipeline and
asset management
Current annual real losses selection,
installation,
maintenance,
renewal,
replacement
FIGURE 17.1 Four potential intervention tools of an active real loss management program.
(Source: IWA Water Loss Task Force and AWWA Water Loss Control Committee.)
Repair Time: This is the time to affect a repair that halts the leakage flow, once the
location of the leak has been identified. This is not just the time of the shutoff or
repair action, but all time needed to route the repair work order, schedule the
repair, notify customers, and other activities, which can take days or weeks
depending upon the policies of the water utility.
Figure 17.2 depicts the impact the awareness, location, and repair time duration
have on the total volume lost from a leak.
1
Figure 17.2 provides the results from a study carried out in England in order to
investigate the impact leak run times of various size leaks have on overall system leak-
age volume. It clearly shows that mains breaks, which due to their disruptive nature are
75 1.1 Days
m 3 /day Reported mains
burst
3
82.5 m
Reported service
m 3 /day 25 A L R connection burst
16 Days
3
400 m
Unreported service
m 3 /day 25 A 182.5 Days L connection burst
3
>4500 m
R
FIGURE 17.2 Impact of awareness, location, and repair time on total leakage volume.
(Source: Ref 1.)