Page 38 - Water Loss Control
P. 38
20 Cha pte r T h ree
usually leakage, are typically valued at the variable production cost of the water.
Apparent losses, which occur at the customer destination, penalize the water sup-
plier at the retail cost; a rate usually much higher than the production cost. The vari-
able production costs frequently include only the short-term costs; however, in many
cases it is appropriate to include long-term costs in the valuation of real losses, the
cost implications of real and apparent losses require that a careful assessment of each
be undertaken to design the most appropriate and cost-effective water loss control
program.
3.1.1 Real Losses
The quantity of real losses in a given water systems is a good indicator of how efficient
a water supplier is in managing its assets (the distribution network) and the product it
delivers to its customers. Volumes of real losses that are significantly higher than what
is economically justifiable indicate that action needs to be taken if the water supplier is
to be viewed as water-efficient, customer-responsive, and a responsible steward of
water resources.
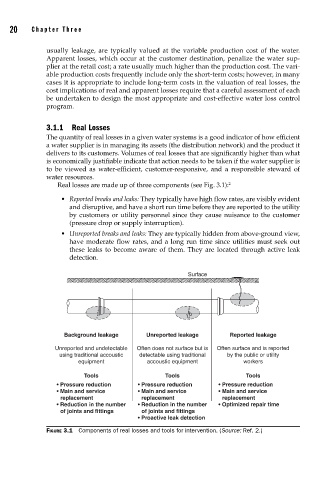
Real losses are made up of three components (see Fig. 3.1): 2
• Reported breaks and leaks: They typically have high flow rates, are visibly evident
and disruptive, and have a short run time before they are reported to the utility
by customers or utility personnel since they cause nuisance to the customer
(pressure drop or supply interruption).
• Unreported breaks and leaks: They are typically hidden from above-ground view,
have moderate flow rates, and a long run time since utilities must seek out
these leaks to become aware of them. They are located through active leak
detection.
Surface
Background leakage Unreported leakage Reported leakage
Unreported and undetectable Often does not surface but is Often surface and is reported
using traditional accoustic detectable using traditional by the public or utility
equipment accoustic equipment workers
Tools Tools Tools
• Pressure reduction • Pressure reduction • Pressure reduction
• Main and service • Main and service • Main and service
replacement replacement replacement
• Reduction in the number • Reduction in the number • Optimized repair time
of joints and fittings of joints and fittings
• Proactive leak detection
FIGURE 3.1 Components of real losses and tools for intervention. (Source: Ref. 2.)