Page 90 - Water and Wastewater Engineering Design Principles and Practice
P. 90
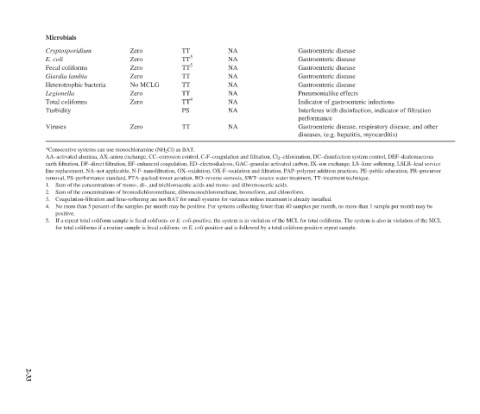
Gastroenteric disease Gastroenteric disease Gastroenteric disease Gastroenteric disease Gastroenteric disease Pneumonialike effects Indicator of gastroenteric infections Interferes with disinfection, indicator of filtration performance Gastroenteric disease, respiratory disease, and other diseases, (e.g. hepatitis, myocarditis)
NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA AA–activated alumina, AX–anion exchange, CC–corrosion control, C-F–coagulation and filtration, Cl 2 –chlorination, DC–disinfection system control, DEF–deatomaceous earth filtration, DF–direct filtration, EF–enhanced coagulation, ED–electrodialysis, GAC–granular activated carbon, IX–ion exchange, LS–lime softening, LSLR–lead service line replacement, NA–not applicable, N-F–nanofiltration, OX–oxidation, OX-F–oxida
TT TT 5 TT 5 TT TT TT TT 4 PS TT removal, PS–performance standard, PTA–packed-tower aeration, RO–reverse osmosis, SWT–source water treatment, TT–treatment technique. 1. Sum of the concentrations of mono-, di-, and trichloroacetic acids and mono- and dibromoacetic acids. 2. Sum of the concentrations of bromodichloromethane, dibromonochloromethane, bromoform, and chloroform. 3. Coagulation-filtration and lime-softening are not BAT for small s
No MCLG
Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero *Consecutive systems can use monochloramine (NH 2 Cl) as BAT.
Microbials Cryptosporidium E. coli Fecal coliforms Giardia lambia Heterotrophic bacteria Legionella Total coliforms Turbidity Viruses positive. 5.
2-33