Page 334 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 334
ION EXCHANGE 8-3
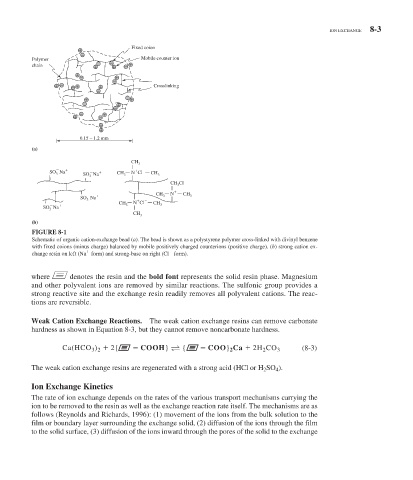
Fixed coion
Polymer Mobile counter ion
chain
Crosslinking
0.15 – 1.2 mm
(a)
CH
3
SO Na SO Na CH 3 N Cl CH 3
3
3
CH Cl
3
CH 3 N CH 3
SO Na
3
CH N Cl CH
3 3
SO Na
3
CH
3
(b)
FIGURE 8-1
Schematic of organic cation-exchange bead ( a ). The bead is shown as a polystyrene polymer cross-linked with divinyl benzene
with fixed coions (minus charge) balanced by mobile positively charged counterions (positive charge). ( b ) strong cation ex-
change resin on left (Na form) and strong-base on right (Cl form).
where denotes the resin and the bold font represents the solid resin phase. Magnesium
and other polyvalent ions are removed by similar reactions. The sulfonic group provides a
strong reactive site and the exchange resin readily removes all polyvalent cations. The reac-
tions are reversible.
Weak Cation Exchange Reactions. The weak cation exchange resins can remove carbonate
hardness as shown in Equation 8-3 , but they cannot remove noncarbonate hardness.
Ca(HCO ) 2{ ź COOH} { ź COO} Ca 2H CO 3 (8-3)
2
3 2
2
The weak cation exchange resins are regenerated with a strong acid (HCl or H 2 SO 4 ).
Ion Exchange Kinetics
The rate of ion exchange depends on the rates of the various transport mechanisms carrying the
ion to be removed to the resin as well as the exchange reaction rate itself. The mechanisms are as
follows (Reynolds and Richards, 1996): (1) movement of the ions from the bulk solution to the
film or boundary layer surrounding the exchange solid, (2) diffusion of the ions through the film
to the solid surface, (3) diffusion of the ions inward through the pores of the solid to the exchange