Page 522 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 522
DISINFECTION AND FLUORIDATION 13-17
1000
Giardia
100
Time, min
10 E. histolytica
Polio Type 1
E. coli
1
0.1 1 10
Free available chlorine, mg/L
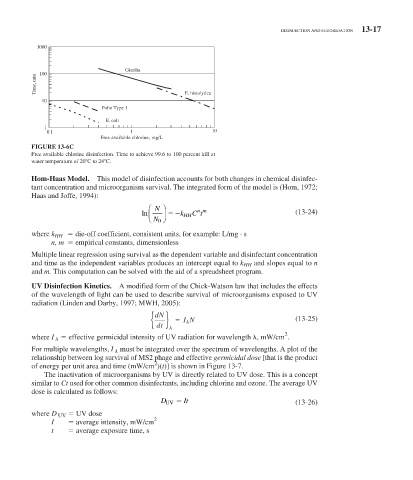
FIGURE 13-6C
Free available chlorine disinfection. Time to achieve 99.6 to 100 percent kill at
water temperature of 20 C to 24 C.
Hom-Haas Model. This model of disinfection accounts for both changes in chemical disinfec-
tant concentration and microorganism survival. The integrated form of the model is (Hom, 1972;
Haas and Joffe, 1994):
⎛ N ⎞
nm
ln ⎜ ⎝ ⎟ ⎠ k HH C t (13-24)
N 0
where k HH die-off coefficient, consistent units, for example: L/mg · s
n, m empirical constants, dimensionless
Multiple linear regression using survival as the dependent variable and disinfectant concentration
and time as the independent variables produces an intercept equal to k HH and slopes equal to n
and m. This computation can be solved with the aid of a spreadsheet program.
UV Disinfection Kinetics. A modified form of the Chick-Watson law that includes the effects
of the wavelength of light can be used to describe survival of microorganisms exposed to UV
radiation (Linden and Darby, 1997; MWH, 2005):
{ } =
IN (13-25)
dN
dt
2
where I
effective germicidal intensity of UV radiation for wavelength , mW/cm .
For multiple wavelengths, I
must be integrated over the spectrum of wavelengths. A plot of the
relationship between log survival of MS2 phage and effective germicidal dose [that is the product
2
of energy per unit area and time (mW/cm )( t )] is shown in Figure 13-7 .
The inactivation of microorganisms by UV is directly related to UV dose. This is a concept
similar to Ct used for other common disinfectants, including chlorine and ozone. The average UV
dose is calculated as follows:
D UV It (13-26)
where D UV UV dose
2
I average intensity, mW/cm
t average exposure time, s