Page 135 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 135
Consequently, the general prototype of this type of calls is
122 Welding Robots
short status call_service_i (struct parameters_i, struct answer_i)
where status returns the service error codes (zero if the service returns without
errors, and a negative number identifying the error otherwise), parameters_i is the
data structure containing the service parameters and answer_i is the data structure
that returns the service execution results.
The asynchronous services, when activated, return answers/results asynchronously,
i.e., the remote system should also make remote procedure calls to the client
system when the requested information becomes available or when the specified
event occurs (system and controller state changes, robot program execution state
change, IO and variable events, etc.). Those calls may be named events or
spontaneous messages, and are remote procedure calls issued to all client
computers that made the correspondent subscription, i.e., made a call to the
subscription service properly parameterized specifying the information wanted. To
receive those calls any remote client must run RPC servers that implement a
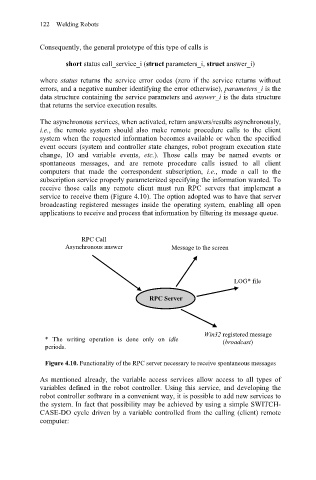
service to receive them (Figure 4.10). The option adopted was to have that server
broadcasting registered messages inside the operating system, enabling all open
applications to receive and process that information by filtering its message queue.
RPC Call
Asynchronous answer Message to the screen
LOG* file
RPC Server
Win32 registered message
* The writing operation is done only on idle (broadcast)
periods.
Figure 4.10. Functionality of the RPC server necessary to receive spontaneous messages
As mentioned already, the variable access services allow access to all types of
variables defined in the robot controller. Using this service, and developing the
robot controller software in a convenient way, it is possible to add new services to
the system. In fact that possibility may be achieved by using a simple SWITCH-
CASE-DO cycle driven by a variable controlled from the calling (client) remote
computer: