Page 309 - Well Control for Completions and Interventions
P. 309
Well Kill, Kick Detection, and Well Shut-In 301
6000.00
Surface pressure
5000.00
4000.00
3000.00
2000.00
1000.00
0.00
0 156
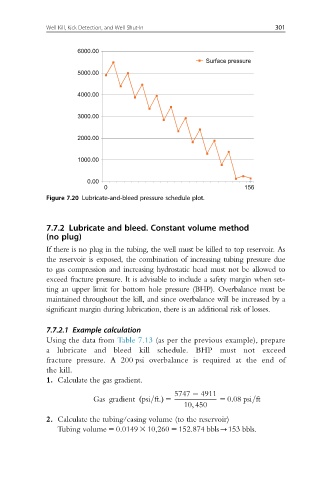
Figure 7.20 Lubricate-and-bleed pressure schedule plot.
7.7.2 Lubricate and bleed. Constant volume method
(no plug)
If there is no plug in the tubing, the well must be killed to top reservoir. As
the reservoir is exposed, the combination of increasing tubing pressure due
to gas compression and increasing hydrostatic head must not be allowed to
exceed fracture pressure. It is advisable to include a safety margin when set-
ting an upper limit for bottom hole pressure (BHP). Overbalance must be
maintained throughout the kill, and since overbalance will be increased by a
significant margin during lubrication, there is an additional risk of losses.
7.7.2.1 Example calculation
Using the data from Table 7.13 (as per the previous example), prepare
a lubricate and bleed kill schedule. BHP must not exceed
fracture pressure. A 200 psi overbalance is required at the end of
the kill.
1. Calculate the gas gradient.
5747 4911
Gas gradient ðpsi=ft:Þ 5 5 0:08 psi=ft
10; 450
2. Calculate the tubing/casing volume (to the reservoir)
Tubing volume 5 0.0149 3 10,260 5 152.874 bbls-153 bbls.