Page 132 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 132
ke
tor
_—
loc
415
by the root mean square velocity (Vays): ¢) The interval velocity (V;.1)
Root mean square velocity. Raypath bending leads to disproportionally long paths in
ve:
as if each ray traveled
travel in the low-velocity (V,) layer leads to a
leads to a long ray segment. The average
«Lower interface
Upper Interface
Processing
Surface
i
R
(V..)
©"
r
rece
Ri
Types of velocity. a) Left: The average velocity of the material above at interface
average velocity is the same
(2)
77,
OTOOOE//
in the layer (At).
to
A,
takes a wave to travel vertically from the surface
Vint
Te
Velocity R.
travel
divided by the travel time spent
TOTO OOOO
PR;
FF
layers. For example, for the bold raypath, near-vertical
layer, more horizontal
Square R,
Pr
Taypaths, assuming no bending due to Snell’s Law. The
Velocity
S;
KR
S,
Mean
a U-shaped raypath is approximated
Interval
WOOO
At
VITO (a
the high-velocity (V3)
Ve>V,
77777?
ie
Az |
layer is the thickness of the layer (Az)
Root
|My
by the time (t) it
Velocity
Va>
7
{\
C)
each layer. b)
b)
zit
short ray segment; in
(2) divided
Average
vertically through
.
high-velocity
5.15
along such
Teflection
interface
FIGURE
a)
a
where: velocity average = Vay the interface above depth = z surface the from interface the to : time travel one-way = t interface. to surface from For Sequence layered a above a reflector, velocity average the envisioned be can according to “V-shaped” rays not do that across interfaces: the
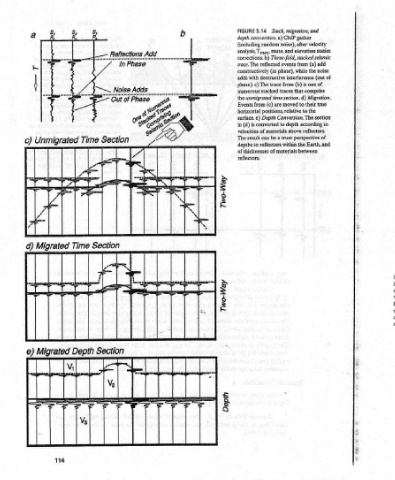
migration, and CMP gather noise), after velocity Three-fold, stacked seismic (a) add events from the noise phase), while destructive interference (out of (b) is one of traces that comprise Migration. to their true Conversion. section The according 1o truer perspective of the Earth, and of materials between
Stack, analysis, Ty49, mute, and elevation statics (in the unmigrated time section. d) are moved (c) positions, relative to the to depth velocities of materials above reflectors. a be
5.14 depth conversion. a) (including random trace. The reflected phase). c) The trace from numerous stacked surface. e) Depth is converted can depths to reflectors within
FIGURE corrections. b) constructively adds with Events from horizontal (d) in The result of thicknesses Teflectors.
ABM-OML ABM -OML yideq
b
Reflections Add Phase In Section Ve
ROR |_— Section Time Depth
S86 V4
a
$ Migrated Migrated 114
d) e)