Page 21 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 21
.
*
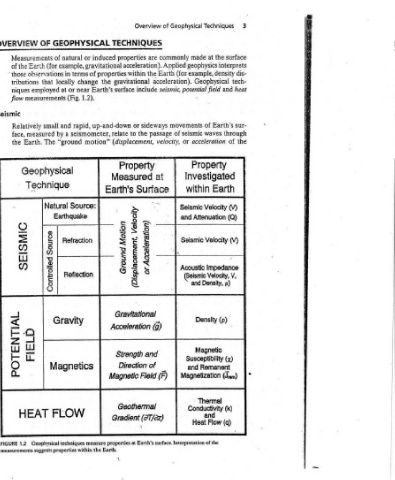
3 surface interprets dis- tech- heat sur- through the of (V) (Q) (V) V, § .
Techniques the at example, density Geophysical and Earth’s of waves acceleration Property Investigated Earth Seismic Velocity Attenuation Seismic Velocity Impedance Velocity, Density, p) Density (p) Magnetic Susceptibility (x) Remanent (Jrem) Thermal Conductivity (k) and (q) Flow
Geophysical made geophysics potential field movements seismic or within and Acoustic (Seismic and and Magnetization Heat
of commonly Earth (for acceleration). seismic, ge of passa velocity, at | G _ | (F)
Overview TECHNIQUES are properties acceleration). Applied the within gravitational include surface sideways or the to relate (displacement, Property Measured Surface Earth's Apojap ‘ueweorsdsjq) Gravitational ag (g) Acceleration Strength and of Direction Field Magnetic Geothermal (AT/z) dient Gradient ( : techniques measure properties at Earth’s surface. Interpretation of the
410
(uoyBsajad0V
uonoy punoi
GEOPHYSICAL induced or natural example, gravitational of properties terms in the change locally Earth’s near or at 1.2). (Fig. up-and-down rapid, and seismometer, a motion” “ground Source: Earthquake Refraction Reflection Gravity Magnetics FLOW the Earth.
OF of Measurements (for Earth observations that employed measurements small by measured The Earth. Geophysical . Technique Natural eoinog pajjouoD HE AT Geophysical measurements suggests properties within
OVERVIEW of the “those tributions niques flow Seismic Relatively face, the s OINSIAS WILNALOd 1.2 FIGURE
q1ala
) Physics en Ns i 2 . nearer a sees materials (geology) with no subsurface information. result a sphere of radius (R) and from mass buried a by such depth (z) below might cause such that (p) result in a predicted gravity topography, the crust/mantle boundary, features through balance within Students Earth. the to interpretations constrain different of the portions Earth.
$
s=+=+=: by combining obsefvations of Earth illustrating surface geology, with would (Ag,) that a model of subsurface density distribution these three depth certain measurements in system book this in basic are the to appreciate Earth’s geochronology, be may
Predicted from Mode] Cross-section Earth’s gravity field predicts the change in gravity caused the observed surface geology and shows density distributions that between transition; a at equalizes of geophysical covered flow) heat them example, but they courses.
Introduction Geology ie Earth's Surface ? the subsurface a) (physics). in equation field. along with relationship the is lithosphere/asthenosphere pressure the utility lithosphere/asthenosphere methods geophysical and magnetics, helping in methods (for important, are advanced geophysics
1 ee (epw) Geophysics aims to interpret phenomena parameter. the change mathematical Observed change in gravity agrees with observed. focus whereby appreciate and crust The gravity, particularly Other methods) more
Chapter a) Ajewouy AyAks5 (Ap). The model to that primary A the and isostasy, thus of the quake, dents, tectonics. electrical or istry
2 1.1 observations of physical b) Model of a physical density contrast
FIGURE the surface. c) a change. The anomaly close