Page 22 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 22
5
Constraints
Surface
‘Surface
Earth's
(F),
Earth's
See ee
of subsurface
(-Ap)
c
magnetic
TECHNIQUES
and
Body
(J,,,,)
Methods
meter measures gravitational
total
Lower g
Density
magnetization
s
the Earth
Interpretation:
Low
reveal
remanent
Magnetometer
local density changes (Ap). Magnetometers
>
FIELD
i ge
g
{
gravity
magnetic susceptibility (x) and
(+Ap)
A
POTENTIAL
Potential field techniques.
g
Body
,
Gravity__ (il:
Higher
a
Density
lcs
Meter
the
by
High
Magne
1.4
to
influenced
materials.
sensitive
FIGURE
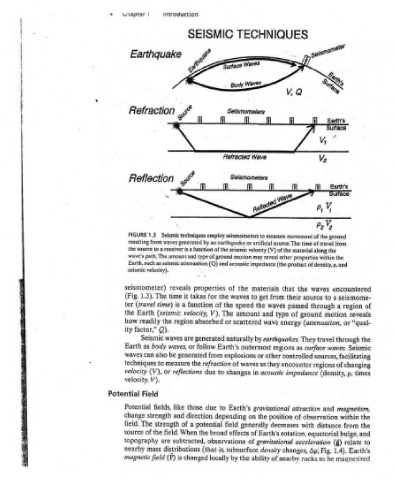
encountered formed they as magnetized been having rocks the by or x) susceptibility, seismome- (magnetic magnetization, Jrem)+ (remanent of region reveals “qual- or Flow Heat one a. to Earth’s regions hotter from outward, flows constantly Heat - : dri in the through downward surface the from measured be can (7) temperature in
Earth's Surface from the the a a motion waves. sources, facilitating (density, (g) 1.4). be
geist V> p2V, movement of the ground time of travel along material within properties product of density, p, and waves the to source passed through ground (attenuation, travel They surface as controlled regions encounter impedance and attraction observation of distance with equatorial acceleration Fig. Ap; rocks to
TECHNIQUES : Selsmometers ff go Wave Selsmometers il i or artificial source. The (V) of the motion other reveal may (the impedance that materials the to their from get waves the speed of type and amount wave scattered energy earthquakes. by outermost regions other or of waves they as acoustic in gravitational position the on decreases generally of Earth’s rotation,
SEISMIC so © Refracted ti fi Seismic techniques employ seismometers to measure earthquake by an of the seismic velocity function type of ground and acoustic (Q) of properties waves the for takes function the of V).The or absorbed naturally generated Earth’s follow explosions from refraction changes to due Earth’s to due direction depending field potential effects broad th
introduction g s? ff eo waves generated receiver is a and amount as seismic attenuation reveals it time a is time) velocity, (seismic region the are waves waves, or generated be the measure reflections or those like and a of strength field. When subtracted, are distributions changed is (F)
i Earthquake Refraction Reflection 1.3 from source a to The path. Earth, such velocity). seismometer) 1.3). The (travel Earth readily Q). factor,” Seismic body as also can to (V), V). Field fields, strength The the of mass magnetic field
Cnapter FIGURE resulting the wave’s seismic (Fig. ter the how ity Earth waves techniques velocity velocity, Potential Potential change field. source topography nearby
+