Page 27 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 27
9
from
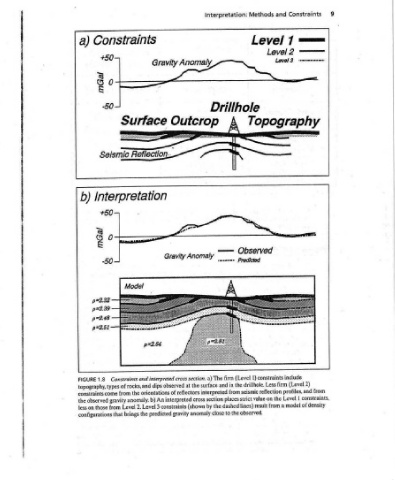
Constraints ,— somemomemes include (Level 2) profiles, and constraints, 1 of density
and Levels 7) Topography nara firm Level the model a from
Methods Level Observed Predicted 1) constraints Less the drillhole. from seismic reflection on value result lines) observed.
Interpretation: Drillhole { ./ C\ —— swomeme a (Level firm a) The in and interpreted places strict the dashed the to close
Anomaly, Outcrop Gravity Anomaly je the surface cross section by (shown
,
Snavitnd ravity Wy Constraints and interpreted cross section. dips observed at orientations of reflectors interpreted An Level 3 constraints predicted gravity anomaly
Constr aints +50 ° 50 Seismic Inte rp. retation +50 0 ? topography, types of rocks, and from observed gravity Level 2. from brings that
: Surface Reflection. Model the b) anomaly. the
a ) jepu b ) & s p=2,.82 p=2.39 p=2.48 p=2.51 1.8 FIGURE constraints come the those less on configurations
;
example, sur- éxample, geo- of models other the Model _ the surface. Surface outcrop resulting in closer to eunane not changed.
hand: (for sense For interpretations suggest in predicted by surface geology are
your observations. levels. further Thinking Predicted from — Model
in common Starting testing subsurface densities and geometries,
put : Earth. direct and 3) (2, constrain region. "Observed Le at several stations on Densities and geometries adjusted
can you the scattered logic lower can interpretations in the Anomaly cick ceed constraints offered
that about on to (1) 1) $0 Model measured c) the
Earth on based based higher (Level geophysical processes b) Observed Predicted Preliminary model that
the observations observations. region or —— rasme= Adjusted density (g/cm?).
of samples. interpretations considerations, from flow a of the structure Gravity anomaly = anomalies. Note
Introduction (Firm Constraints): atkervatioas pe Outcrop cores. Drill Constraints): (Softer or Indirect inferred Map Geophysical (Reasonable Assumptions): Theoretical “modeling”). should mapping 2); (Level data overall for Gravity Anomaly § #0 a) Forward modeling example. interpretation. b) (see Chapter 8). p and predicted
Chapter 1 1: Level a) b) 2: Level a) b) 3: Level Thinking face geological physical 3) (Level es and dips serve as constraints on a predicted gravity anomaly between observed
8 1.7
ydg —=— FIGURE agreement
;
nn eter ee ee