Page 234 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 234
continents.
broken
is
upper
217
veloci-
km/s,
material.
Moho
8
The
wave
over
Interior
be
The
underlying
can
under
2.7).
velocities just
S
km/s.
and
It
Earth’s
Fig.
solid.
km)
-
P
8
10%;
and
depth),
kmdepth.
about
70
of
soft, “plastic”
lithosphere
to
Probes
P-wave
to
(20
to
km
(1%
km/s
deeper
to 200
as
300
lithosphere), with
Waves
melted
overlying
to
is a
6-7
100
much
100
asthenosphere
Seismic
to
from
partially
(about
down
but
the
abruptly,
oceans,
for
crust
part
(or mantle
be
than
may
upper
of the
The
beneath
increase
lower
zone
uppermost mantle
base
Asthenosphere
the
deep
6%
In
low-velocity
velocities
the
parts.
about
from
km
two
10
extends
are
P-wave
about
This
into
The
ties
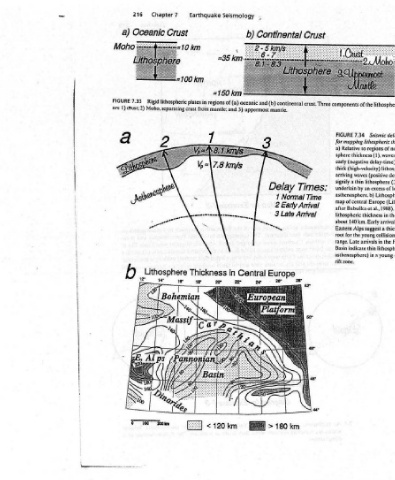
lithosphere tigid more the which ), over low (relatively substratum soft a thus is asthenosphere km 700 to 300 (about asthenosphere of the part lower the In ride. plates lithospheric shear in increase an suggesting increase, gradually velocities wave S and P depth), (Figs. 2.7, 2.8). strength times arrival analyzing by mapped be can plates Seismic delay-time method lit
7.34 thick (high-velocity) thin asthenosphere. b) et lithospheric thickness 140 km. Eastern Alps suggest a Late arrivals in thin in
FIGURE Relative a) sphere signify a underlain map of central after BabuSka about root for the range. Basin indicate asthenosphere) rift zone.
Crust Times: Time Early Arrival Late Arrival 2°
Continental regions of (a) oceanic and (b) continental crust. Three components of the Delay Normal 1 2 3 Europe km 180 >
* b) uppermost mantle. Central
Seismology km #150 from mantle; and 3) in ewe
= Earthquake Thickness
Chapter? Crust Rigid lithospheric plates in Moho, separating crust _Uthosphere ewe
216 Oceanic 7.33 l) ctust;2)
FIGURE are
a) b