Page 63 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 63
ae Earth. well par- layer- velocity The wave. under- means 45
from the as are 4) uppermost of details of earthquake waves. seismic it behavior acm oust —> on on seria “ 2 u they
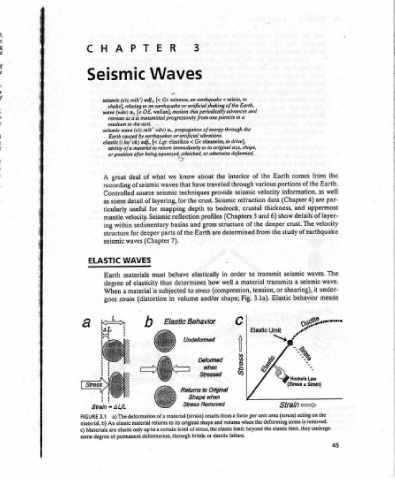
the Earth comes of portions of various information, velocity seismic (Chapter refraction data and thickness, crustal show 6) and 5 crust. The deeper the of study the from seismic transmit to a a material transmits shearing), or tension, Elastic 3.1a). Fig. ye Umit Elastic 4 “Se \ z Strain area (stress) per unit the deforming — limit, elastic the
Gr. seismos, an earthquake < seiein, (0 earthquake or artificial shaking of the Earth. that periodically advances and energy through the of : Lgr. elastikos < Gr. clauneim, to drive), immediately to its original size, shape, interior the about through traveled provide Seismic crust. bedrock, to (Chapters profiles structure gross determined are Earth 5 order in elastically well how
TER Waves = [< wafian], motion OE. retreats as it is transmitted progressively from one particle in a n., wav) Earth caused by earthquakes or artificial vibrations. (< adj., or position after being squeezed, stretched, or otherwise deformed. ord we what of waves seismic source layering, of mapping for Seismic basins sedimentary parts deeper (Chapter 7). behave must thus elasticity sub
8 propagation know have that techniques the for depth reflection and of the determines to volume 3 Retums Shape (strain) to its original shape and of level
vv
5
AP CH Seismic seismic (siz mik’) adj., shake}, relating to an [< n., wave (wav) medium to the next. seismic wave (siz mik' elastic (i las’ tik) ability of a material to return deal great A recording of seismic Controlled detail some as useful ticularly velocity. mantle within ing for structure waves seismic WAVES ELASTIC materials Earth of degree material a When strain goes AL/L
1989, time: Geothermal Cretaceous/ struc- of J. D, in Marine and the Initial of 327, lower rift- 94, at Brocher, seamount
Peterson, Tertiary Program, Leg eastern Snake Journal and Webb, archipelagic aprons islands, 55, leg experiment, motions v. Nature, the in early the v. Yellowstone Geothermal lithosphere of lithospheric
L. through Drilling and D. G. Pyle, 1988, Rapid eruption of at the the Idaho, E 16, pp. 385-406. 1980, Introduction DSDP Drilling Project, v.55, pp.3-31. Relative Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans plumes and Tectonophysics, 1994, The and the
and Volcanology 1982, Compressional wave velocity under H. and Hawaiian from 1987, time, tracks of Brink, P. Buhl and T. M. Hawaiian-Emperor 105-111.
Backman activity Ocean 193-198. basalts Tertiary boundary, Nature, v. 333, pp. 841-843. km 350 Rexburg, Geophysical Research, v. 87, pp. 2654-2670. McNutt, and others, hot-spot Stock, Cretaceous Convection Hotspot Atlantic, Braile, of Volcanology 121-187. Flexure Hawaii, Tectonophysics, v.9, pp. 435-446. multichannel seismic study
J. hotspot from of flood upper near K. 1993, Volcanism and results J. 1971, mantle, Nature, v. 230, pp. 42-43. 1983, L. W. 1970, the
A., results Journal Plain M. Marquesas Geophysical Research, v. D., of and the the and I., across chain, Nature, v. 315, pp.
R. Reunion Research, v.36, pp. Duncan, R. A.,and Deccan of the E., P. E. Hawaiian-Emperor Reports Deep Sea P, hotspots in late pp. 587-591. W. J., of 123-139. B., Hotspot, Journal Research, v. 61, pp, R. Watts, A. B., U.S. ten
Duncan, Initial 115, the Evans, J. R., ture River Filmer, Dixon, the Jackson, summary Molnar, since Morgan, Morgan, W. J., ing pp. R. Smith, Walcott, 1985, A flexure
* tectonics of the upper Ventura of Association 1353-1373. observed on seismic- A California, 75 . v. faults, Geological their bear- exam- New of Island, Ranges, comparison, heat of northwestern 323-343, tectonics mechanism Seismological southern for Tectono-
Tectonics area, Mountain Brown, 1988, Variable crustal as zones 100, pp. 665-676. 1985, profile across the San Andreas, Sargent, west-central of America, to folding with Royal Society 1987, South Transverse implications Plain, 164, pp. Block 1991, focal a Bulletin in the reference of continents,
Plate Sulphur American Geologists Bulletin, v.75, pp. L. D. strike-slip fault deep seismic reflection profiles, Geological Society Colbum, R..H. faults, Society : 1988, Strike-slip Society of America Bulletin, v. 100, pp. 1666-1703. new class of faults and ing on continental drift, Nature, v.207, pp. 343-347. related Zealand, Zealand Bulletin, v.24, pp. 273-291. Berryman, R. and the seismotectonic ~ Reg
Chapter2 Huftile, G. J., 1991, Thin-skinned and Valley California, Petroleum Lemiszki, P. J. and structure of of America Bulletin, v. D., W. and refraction Calaveras Seismological pp. 175-191. G., A. Wilson, J.T., 1965, A 1986, Faults from New and R. S., K. Zealand, California: A Tectonics, v. 6, pp. 363-376. Hotspot Settings 1989, D., D. of Snake the States, C. and C. J., of i
44 Ojai Basin, Mooney, and Bulletin Sylvester, Yeats, R. S., ples Yeats, New Blackwell, flow United 1989. + Bryan, the of analysis Duncan, motion