Page 65 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 65
;
,
‘
47 that and (for of to the the be P,
Earth their under direc- volume divided ‘ change to is of the the Earth. Material
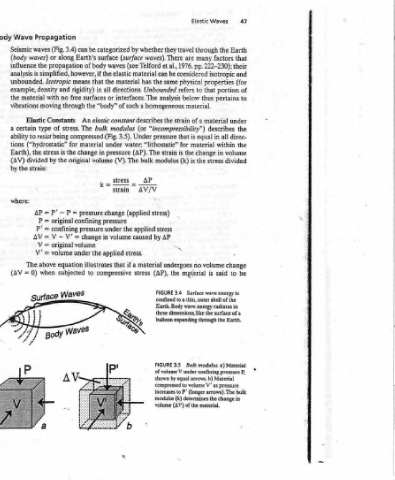
Waves the factors 222-230); isotropic properties portion that pertains material describes all in within in stress volume said is energy wave radiates in a) Material (Jonger arrows). The bulk
Elastic through many are pp. 1976. considezed physical to refers thus below material. of a strain equal is that material for change the is the is (k) no material Surface confined to a thin, outer shell Earth. Body wave energy three dimensions, like the surface of a balloon expanding through Bulk modulus. of volume V under confining pressure arrows. b) compressed to volume V' as pressur
by whether they travel waves). There (see Telford al., et be can material same the has Unbounded analysis homogeneous a the “incompressibility”) (or Under pressure “lithostatic” strain (AP). The modulus bulk AP AV/V . rey ein stress applied AP by caused undergoes material (AP), stress the 3.4 FIGURE 3.5 FIGURE shown by equal increases to P’
categorized (surface surface waves elastic material the directions. all interfaces. The or of such “body” elastic constant describes modulus 3.5). water; under pressure (V). The Stress _ sain Eaves ees the under volume in stress. applied a if that compressive
be body that in surfaces the bulk material in change volume k its pressure change the illustrates to
can 3.4) Earth’s of is simplified, however, if the means rigidity) free through An The stress. resist being compressed.(Fig. for the original pi Panna = V' volume under equation subjected
Propagation (Fig. along or propagation the Isotropic and density no with moving Constants of type (“hydrostatic” is stress the by peop! ot 5 : es x poicen al ' = confining — V AV = It original V = ul volume V’ = above when
Wave Seismic waves waves) (body influence analysis unbounded. example, material the vibrations Elastic certain to ability tions the Earth), divided (AV) strain: the by where: ‘ P’ The 0) = (AV
Body a
:
is of the shows of parti- flows an of the an few results in rates, as
stress amount others. deforming time level that removed. as from elastically a underlying remain connected strain (ductile) of overlying
the the under the of 3.1¢ Fig. certain so is material rupturing behavior results only at the Inelastic
when where inelastic of length rate). a to fails, stress the the behaves move motion, a) During ductile particles Brittle deformation
shape 3.1c). orientation the 2) (strain up only material the whereby lithosphere by of particles plates this flow. b) the development of fractures. a) Elastic behavior occurs at very high of seismic waves. b)
and behavior (Fig. conditions, and Law) the when ductile, the illustrated movement asthenosphere with fashion. oe 3.2 formation and
volume elastic of stress some and shearing); of distortion Hooke’s limit that positions be or breaking is rate) rapid the Lithospheric associated (ductile) the passage
original describes amount under magnitude or tension, amount (obeying Beyond original may limit pencil (that is, strain very rates strain waves. rates ; in very slow straining of the asthenosphere; viscous flow facilitates the movement
its Law the to elastic the 1) certain limit. a but seismic inelastic b) Brittle Deformation
to be elastic their elastic like time Small high strain an
Waves returns Hooke’s proportional may are: compression, a achieve be elastic to the brittle, of 3.3). very transmit slow in Elastic and inelastic behavior of the asthenosphere. by an earthquake; the vibrations result
Seismic material 3.1b). (Fig. linearly materials factors of (amount to takes may material the as return not beyond or putty, 3.2). (Fig. importance (Fig. these at to able very the deforms 325 i] 4s s-=-=*”' -“Asthenosphere
Chapter 3 the that removed is strain Earth important Two stress material a that known stress, do cles Deformation silly like earthquake The asthenosphere earthquake; thus is and at cm/year; asthenosphere a) Ductile - Deformation go moe oN. x emo
FIGURE
46 3.3 particles are vibrated behavior results from lithospheric plates.