Page 69 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 69
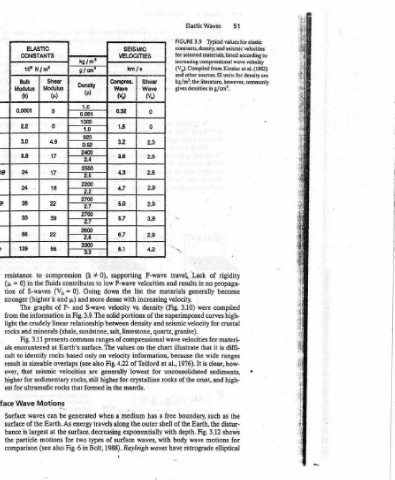
values for elastic seismic velocities according to (1982) units for desiaty are
51 from Kinsler et al. kg/m?; the literature, however, commonly rigidity propaga- become compiled high- crustal materi- diffi- is ranges how- sediments, high- the as distur- shows for elliptical
Elastic Waves Typical 3.9 Constants, density, and listed materials, increasing compressional wave velocity Otties ources SI gives densities in g/cm’. of Lack no in generally were curves for for velocities it that wide the clear, is It and crust, such Earth, the 3.12 Fig. motions wave retrograde
FIGURE for selected (V,). Compiled and travel, results velocity. 3.10) superimposed seismic velocity illustrate because 1976). unconsolidated of the boundary, of the depth. body
Hh P-wave and materials (Fig. of the and limestone, quartz, granite). wave chart al., et for rocks free a shell with with have waves
SEISMIC VELOCITIES km fs Shear | Compres. Wave Wave | v) 0 = 0 15 23 3.2 2.6 3.6 2.6 43 2.9 47 5.0 29 3.8 57 29 6.7 42 84 supporting velocities P-wave the list the increasing with dense density vs. velocity portions solid density between ranges of compressional the on values information, velocity of Telford 4.22 lowest generally crystalline for mant
; kg/m Jom? 9 Denstty (e) 1.0 0.001 . 1.0 aS O82 A = an 27 a 2600 56 ~~ 0), # (k low to contributes down Going 0). = more and ,.) S-wave and P- Fig. 3.9. The in relationship (shale, sandstone, salt, common surface. The Earth’s on only based Fig. also (see overlaps velocities are higher rocks, still in formed th
ELASTIC CONSTANTS N/m? 10° Shear Bulk Modulus }| Modulus ) ) 0.0001 : 0 0 22 49 3.0 17 8.8 17 24 18 24 22 38 39 33 22 88 58 139 compression to resistance fluids the in 0) = S-waves of (V, and k (higher stronger of graphs The information the from linear crudely the light minerals and rocks presents 3.11 Fig. a
Ai ir Water Ice Shale Sandstone Salt Limestone Quarts Granite Peridotite (yw tion als cult est Surface the
'
>
a waves and the or same The the the lack air, the core, in com- both even more than con- to and some
dilated; of propa- “Qn or waves, “S” seismo]- In ce “speed, on resistant the 2) seismic of part than 0). This like through outer increase better rocks, density. As and more becomes fluid melt) therefore down- have
then direction ” direction. or depend more incompressibility by: For 1) waves. example, mantle .) (higher = (y. fluids, slower fluid an to are increasing for and increase rock a less partial waves lithosphere, listed water)
compressed the to “ “secondary” compressional and component, velocities material. The given are generalizations. compressional For the rigid through travel (the lead materials incompressible, true velocity incompressible space, has and (or liquid Seismic mantle substances, and (air
is as initial seismic material’s + 2p 2p p velocities. into more shear strength travel waves material generally As commonly between more commonly pore lithified from V.. the various
air air. to motions. magnitude magnitude the the velocities pe is is and to fluids
the the perpendicular the of rc than wave asthenosphere no cannat same core)... Earth. and 2) decreasing more Vp for
as in referred after particle both the to material, (p) greater wave _ = [u p wave following slower S and lithosphere have waves compressional the inner following factors the rigid generalization relationship become and (k Change both asthenosphere velocity. The
propagates changes are wave also are earthquake their with refer to implied. unbounded density and the is, Body 4Bm fet fet aBu p compressional wave. the to travel P the the from mantle or gasses) shear b) of state the solid within more inverse generally constants With generally is 4) wp. and raising the core. properties
sound density shear a waves an of vector, a used v) and (that travel. = y, p= shear lead always higher travel the (liquids a) and core; solid the than the that depth become This density. an they elastic Decreasing porosity. it time, k both increases, from inner physical P-wave
Waves The the senses for Shear from because to refers commonly necessarily isotropic, E 4, deformation waves the of the the of equations will the they that Fluids things: outer through lower V> suggest Increasing they in show dense, same (yw) traveling the to typical increasing
Seismic through air. eardrum motions 3.8b). arrive they “transverse” waves Waves Body velocity yee is not elastic, an (k, constants to is faster velocity = velocity = velocity waves shear material, the as up lithosphere, suggesting 3) two means Earth’s than Observations 1) velocity. cemented, Increase equations more corresponding 3) (p). the At increasing rigidity while core
Chapter3 traveling person’s Particle : (Fig. gation because as of The form “velocity” ogy direction with For elastic the material rigidity), the and: where: Vp V, The material, rigid more speed waves asthenosphere. rigidity of and water state liquid example, has for seismic and pacted p. 2) and k the though become rocks the rigid; density the dense. more thereby tent,
term
50 Velocity