Page 200 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 200
Section 5.3 Elastic Deformation 201
Table 5.1 Characteristics of the Various Types of Deformation
Type of Deformation Time Dependent? Additional Distinguishing Characteristics
Elastic No Recovered instantly
Plastic No Not recovered
Steady-state creep Yes Constant rate; not recovered
Transient creep Yes Decreasing rate; may be recovered
σ
σ 1 2 σ ε e + ε p 1 ε c 2
time
0 3 4
ε creep recovery
ε e 4 3
0 ε
ε p ε a ε e
t
0
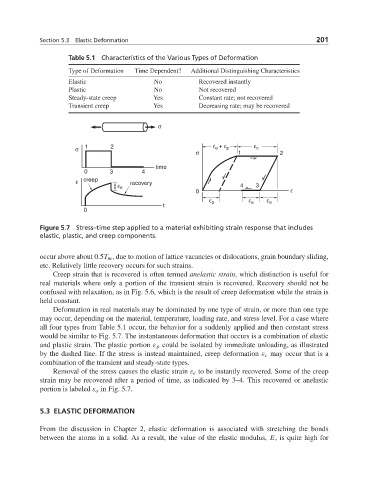
Figure 5.7 Stress–time step applied to a material exhibiting strain response that includes
elastic, plastic, and creep components.
occur above about 0.5T m , due to motion of lattice vacancies or dislocations, grain boundary sliding,
etc. Relatively little recovery occurs for such strains.
Creep strain that is recovered is often termed anelastic strain, which distinction is useful for
real materials where only a portion of the transient strain is recovered. Recovery should not be
confused with relaxation, as in Fig. 5.6, which is the result of creep deformation while the strain is
held constant.
Deformation in real materials may be dominated by one type of strain, or more than one type
may occur, depending on the material, temperature, loading rate, and stress level. For a case where
all four types from Table 5.1 occur, the behavior for a suddenly applied and then constant stress
would be similar to Fig. 5.7. The instantaneous deformation that occurs is a combination of elastic
and plastic strain. The plastic portion ε p could be isolated by immediate unloading, as illustrated
by the dashed line. If the stress is instead maintained, creep deformation ε c may occur that is a
combination of the transient and steady-state types.
Removal of the stress causes the elastic strain ε e to be instantly recovered. Some of the creep
strain may be recovered after a period of time, as indicated by 3–4. This recovered or anelastic
portion is labeled ε a in Fig. 5.7.
5.3 ELASTIC DEFORMATION
From the discussion in Chapter 2, elastic deformation is associated with stretching the bonds
between the atoms in a solid. As a result, the value of the elastic modulus, E, is quite high for