Page 201 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 201
202 Chapter 5 Stress–Strain Relationships and Behavior
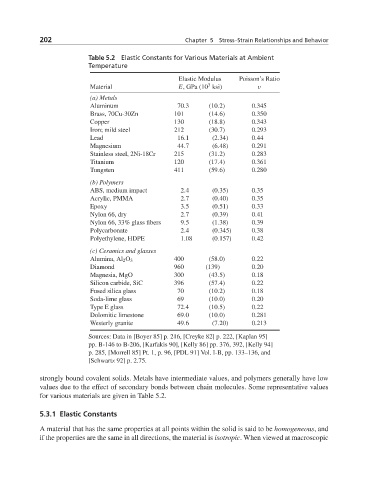
Table 5.2 Elastic Constants for Various Materials at Ambient
Temperature
Elastic Modulus Poisson’s Ratio
3
Material E,GPa (10 ksi) ν
(a) Metals
Aluminum 70.3 (10.2) 0.345
Brass, 70Cu-30Zn 101 (14.6) 0.350
Copper 130 (18.8) 0.343
Iron; mild steel 212 (30.7) 0.293
Lead 16.1 (2.34) 0.44
Magnesium 44.7 (6.48) 0.291
Stainless steel, 2Ni-18Cr 215 (31.2) 0.283
Titanium 120 (17.4) 0.361
Tungsten 411 (59.6) 0.280
(b) Polymers
ABS, medium impact 2.4 (0.35) 0.35
Acrylic, PMMA 2.7 (0.40) 0.35
Epoxy 3.5 (0.51) 0.33
Nylon 66, dry 2.7 (0.39) 0.41
Nylon 66, 33% glass fibers 9.5 (1.38) 0.39
Polycarbonate 2.4 (0.345) 0.38
Polyethylene, HDPE 1.08 (0.157) 0.42
(c) Ceramics and glasses
Alumina, Al 2 O 3 400 (58.0) 0.22
Diamond 960 (139) 0.20
Magnesia, MgO 300 (43.5) 0.18
Silicon carbide, SiC 396 (57.4) 0.22
Fused silica glass 70 (10.2) 0.18
Soda-lime glass 69 (10.0) 0.20
Type E glass 72.4 (10.5) 0.22
Dolomitic limestone 69.0 (10.0) 0.281
Westerly granite 49.6 (7.20) 0.213
Sources: Data in [Boyer 85] p. 216, [Creyke 82] p. 222, [Kaplan 95]
pp. B-146 to B-206, [Karfakis 90], [Kelly 86] pp. 376, 392, [Kelly 94]
p. 285, [Morrell 85] Pt. 1, p. 96, [PDL 91] Vol. I-B, pp. 133–136, and
[Schwartz 92] p. 2.75.
strongly bound covalent solids. Metals have intermediate values, and polymers generally have low
values due to the effect of secondary bonds between chain molecules. Some representative values
for various materials are given in Table 5.2.
5.3.1 Elastic Constants
A material that has the same properties at all points within the solid is said to be homogeneous, and
if the properties are the same in all directions, the material is isotropic. When viewed at macroscopic