Page 263 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 263
Section 6.6 Complex States of Strain 265
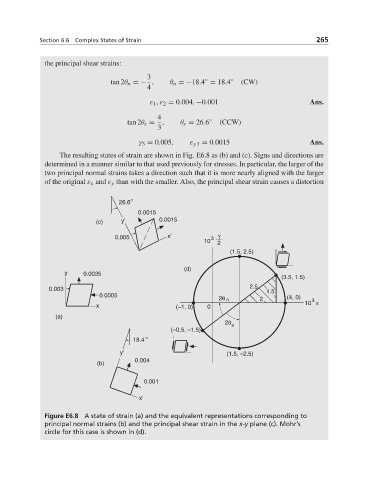
the principal shear strains:
3
tan 2θ n =− , θ n =−18.4 = 18.4 ◦ (CW)
◦
4
ε 1 ,ε 2 = 0.004, −0.001 Ans.
4
tan 2θ s = , θ s = 26.6 ◦ (CCW)
3
γ 3 = 0.005, ε γ 3 = 0.0015 Ans.
The resulting states of strain are shown in Fig. E6.8 as (b) and (c). Signs and directions are
determined in a manner similar to that used previously for stresses. In particular, the larger of the
two principal normal strains takes a direction such that it is more nearly aligned with the larger
of the original ε x and ε y than with the smaller. Also, the principal shear strain causes a distortion
26.6 o
0.0015
(c) y' 0.0015
0.005 x' 3 γ
10 2
(1.5, 2.5)
(d)
y 0.0035
(3.5, 1.5)
2.5
0.003 1.5
0.0005 (4, 0)
2θ n 2 3
x (–1, 0) 0 10 ε
(a)
2θ s
(–0.5, –1.5)
18.4 o
y' (1.5, –2.5)
0.004
(b)
0.001
x'
Figure E6.8 A state of strain (a) and the equivalent representations corresponding to
principal normal strains (b) and the principal shear strain in the x-y plane (c). Mohr’s
circle for this case is shown in (d).