Page 275 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 275
276 Chapter 7 Yielding and Fracture under Combined Stresses
In the present chapter, failure criteria will be considered on the basis of values of stress. Their
application involves calculating an effective value of stress that characterizes the combined stresses,
and then this value is compared with the yield or fracture strength of the material. A given material
may fail by either yielding or fracture, depending on its properties and the state of stress, so that, in
general, the possibility of either event occurring first must be considered.
7.1.1 Need for Failure Criteria
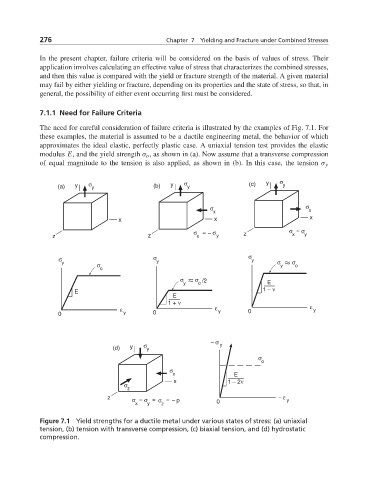
The need for careful consideration of failure criteria is illustrated by the examples of Fig. 7.1. For
these examples, the material is assumed to be a ductile engineering metal, the behavior of which
approximates the ideal elastic, perfectly plastic case. A uniaxial tension test provides the elastic
modulus E, and the yield strength σ o , as shown in (a). Now assume that a transverse compression
of equal magnitude to the tension is also applied, as shown in (b). In this case, the tension σ y
(a) y σ y (b) y σ y (c) y σ y
σ σ
x x
x x x
σ − σ z σ σ
z z x y x y
σ σ σ y
y σ y σ ≈ σ o
y
o
σ ≈ σ /2
y o E
1 − ν
E
E
1 + ν
ε ε ε y
0 y 0 y 0
− σ
(d) y σ y y
σ
o
σ
x E
x 1 − 2ν
σ
z
z σ σ σ − p − ε y
x y z 0
Figure 7.1 Yield strengths for a ductile metal under various states of stress: (a) uniaxial
tension, (b) tension with transverse compression, (c) biaxial tension, and (d) hydrostatic
compression.