Page 325 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 325
326 Chapter 7 Yielding and Fracture under Combined Stresses
(a) What is the safety factor against yielding if the material is ASTM A514 (T1) structural
steel.
(b) Is the design adequate? If not, suggest a new choice of material.
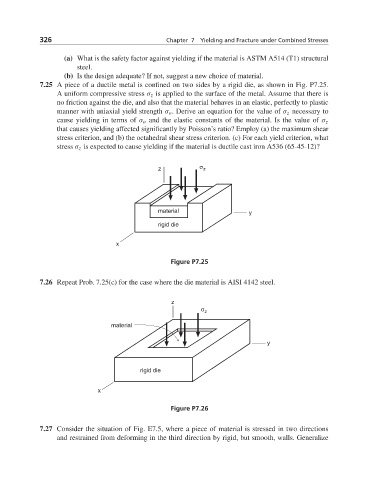
7.25 A piece of a ductile metal is confined on two sides by a rigid die, as shown in Fig. P7.25.
A uniform compressive stress σ z is applied to the surface of the metal. Assume that there is
no friction against the die, and also that the material behaves in an elastic, perfectly to plastic
manner with uniaxial yield strength σ o . Derive an equation for the value of σ z necessary to
cause yielding in terms of σ o and the elastic constants of the material. Is the value of σ z
that causes yielding affected significantly by Poisson’s ratio? Employ (a) the maximum shear
stress criterion, and (b) the octahedral shear stress criterion. (c) For each yield criterion, what
stress σ z is expected to cause yielding if the material is ductile cast iron A536 (65-45-12)?
z σ z
material y
rigid die
x
Figure P7.25
7.26 Repeat Prob. 7.25(c) for the case where the die material is AISI 4142 steel.
z
σ
z
material
y
rigid die
x
Figure P7.26
7.27 Consider the situation of Fig. E7.5, where a piece of material is stressed in two directions
and restrained from deforming in the third direction by rigid, but smooth, walls. Generalize