Page 392 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 392
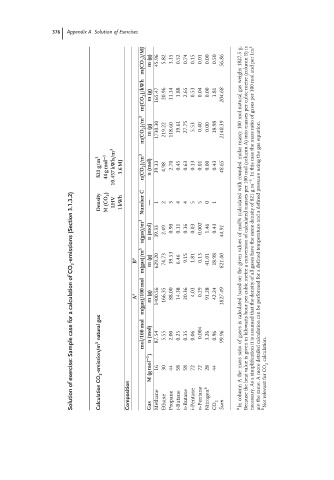
376 Appendix A Solution of Exercises
m(CO 2 )/MJ m (g) 45.96 5.82 3.15 0.52 0.74 0.15 0.01 0.00 0.50 56.86 1827.5g. weighs
m(CO 2 )/kWh m (g) 165.47 20.96 11.34 1.88 2.65 0.53 0.04 0.00 1.81 204.68 gas natural
m(CO 2 )/m 3 m (g) 1730.30 219.22 118.60 19.61 27.75 5.53 0.40 0.00 18.98 2140.39 mol 100 mass):
821 g/m 3 44 g mol −1 10.457 kWh/m 3 3.6MJ n(CO 2 )/m 3 n (mol) 39.33 4.98 2.70 0.45 0.63 0.13 0.01 0.00 0.43 48.65 molar rounded
3.1.3.2) Density M (CO 2 ) LHV 1kWh Number C — 1 2 3 4 4 5 5 0 1 with (calculated
(Section n(gas)/m 3 n (mol) 39.33 2.49 0.90 0.11 0.16 0.03 0.002 1.46 0.43 44.91 mol% of Because the heat value is given in kilowatts hour per cubic metre a conversion of calculated masses per 100 mol (column A) into masses per cubic metre (column B) is necessary. As a simplification it is assumed that the density of all gases have the s
CO 2 -emissions B a m(gas)/m 3 m (g) 629.20 74.73 39.53 6.46 9.15 1.81 0.13 41.01 18.98 821.00 values given are the same. A more detailed calculation can be performed for a defined temperature and a defined pressure using the gas equation.
of the on
calculation A a m(gas)/100 mol m (g) 1400.56 166.35 88.00 14.38 20.36 4.03 0.29 91.28 42.24 1827.49 based
a calculated
for is
case natural gas mol/100 mol n (mol) 87.54 5.55 2.00 0.25 0.35 0.06 0.004 3.26 0.96 99.96 gases
Sample of ratio calculation.
exercise: Calculation CO 2 -emission/m 3 M (g mol −1 ) 16 30 44 58 58 72 72 28 44 mass the
of A b Not relevant for CO 2
Solution Composition Gas Methane Ethane Propane i-Butane n-Butane i-Pentane n-Pentane Nitrogen b CO 2 Sum a In column