Page 142 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 142
Biological Approach for Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutants 123
conservation of these systems in a given animal group conceivably increases the
likelihood that these pharmaceuticals will be pharmacologically active in non-target
living organisms. This method of activity (MoA) idea can be related to all aquatic
biota that are inadvertently exposed to pharmaceuticals in their natural habitat, along
these lines raising the hazard of ecotoxicological impacts.
7.4 PATHWAY FOR PHARMACEUTICAL ITEMS
GOING INTO THE GROUNDWATER
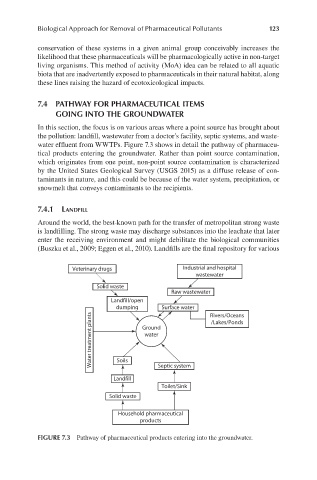
In this section, the focus is on various areas where a point source has brought about
the pollution: landfill, wastewater from a doctor’s facility, septic systems, and waste-
water effluent from WWTPs. Figure 7.3 shows in detail the pathway of pharmaceu-
tical products entering the groundwater. Rather than point source contamination,
which originates from one point, non-point source contamination is characterized
by the United States Geological Survey (USGS 2015) as a diffuse release of con-
taminants in nature, and this could be because of the water system, precipitation, or
snowmelt that conveys contaminants to the recipients.
7.4.1 lanDfill
Around the world, the best-known path for the transfer of metropolitan strong waste
is landfilling. The strong waste may discharge substances into the leachate that later
enter the receiving environment and might debilitate the biological communities
(Buszka et al., 2009; Eggen et al., 2010). Landfills are the final repository for various
Veterinary drugs Industrial and hospital
wastewater
Solid waste
Raw wastewater
Landfill/open
dumping Surface water Rivers/Oceans
Water treatment plants Ground
/Lakes/Ponds
water
Soils
Landfill Septic system
Toilet/Sink
Solid waste
Household pharmaceutical
products
FIGURE 7.3 Pathway of pharmaceutical products entering into the groundwater.