Page 308 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 308
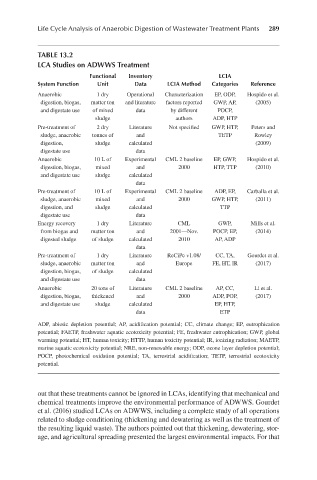
Life Cycle Analysis of Anaerobic Digestion of Wastewater Treatment Plants 289
TABLE 13.2
LCA Studies on ADWWS Treatment
Functional Inventory LCIA
System Function Unit Data LCIA Method Categories Reference
Anaerobic 1 dry Operational Characterization EP, ODP, Hospido et al.
digestion, biogas, matter ton and literature factors reported GWP, AP, (2005)
and digestate use of mixed data by different POCP,
sludge authors ADP, HTP
Pre-treatment of 2 dry Literature Not specified GWP, HTP, Peters and
sludge, anaerobic tonnes of and TETP Rowley
digestion, sludge calculated (2009)
digestate use data
Anaerobic 10 L of Experimental CML 2 baseline EP, GWP, Hospido et al.
digestion, biogas, mixed and 2000 HTP, TTP (2010)
and digestate use sludge calculated
data
Pre-treatment of 10 L of Experimental CML 2 baseline ADP, EP, Carballa et al.
sludge, anaerobic mixed and 2000 GWP, HTP, (2011)
digestion, and sludge calculated TTP
digestate use data
Energy recovery 1 dry Literature CML GWP, Mills et al.
from biogas and matter ton and 2001—Nov. POCP, EP, (2014)
digested sludge of sludge calculated 2010 AP, ADP
data
Pre-treatment of 1 dry Literature ReCiPe v1.08/ CC, TA, Gourdet et al.
sludge, anaerobic matter ton and Europe FE, HT, IR (2017)
digestion, biogas, of sludge calculated
and digestate use data
Anaerobic 20 tons of Literature CML 2 baseline AP, CC, Li et al.
digestion, biogas, thickened and 2000 ADP, POP, (2017)
and digestate use sludge calculated EP, HTP,
data ETP
ADP, abiotic depletion potential; AP, acidification potential; CC, climate change; EP, eutrophication
potential; FAETP, freshwater aquatic ecotoxicity potential; FE, freshwater eutrophication; GWP, global
warming potential; HT, human toxicity; HTTP, human toxicity potential; IR, ionizing radiation; MAETP,
marine aquatic ecotoxicity potential; NRE, non-renewable energy; ODP, ozone layer depletion potential;
POCP, photochemical oxidation potential; TA, terrestrial acidification; TETP, terrestrial ecotoxicity
potential.
out that these treatments cannot be ignored in LCAs, identifying that mechanical and
chemical treatments improve the environmental performance of ADWWS. Gourdet
et al. (2016) studied LCAs on ADWWS, including a complete study of all operations
related to sludge conditioning (thickening and dewatering as well as the treatment of
the resulting liquid waste). The authors pointed out that thickening, dewatering, stor-
age, and agricultural spreading presented the largest environmental impacts. For that