Page 50 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 50
Ecological Assessment 31
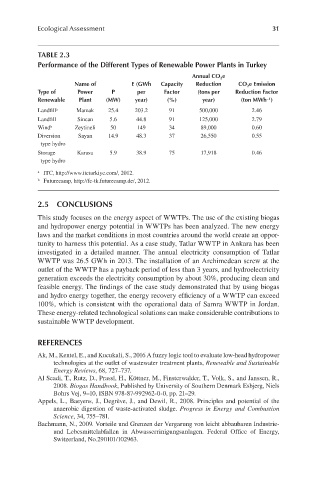
TABLE 2.3
Performance of the Different Types of Renewable Power Plants in Turkey
Annual CO 2 e
Name of E (GWh Capacity Reduction CO 2 e Emission
Type of Power P per Factor (tons per Reduction Factor
Renewable Plant (MW) year) (%) year) (ton MWh )
−1
Landfill a Mamak 25.4 203.2 91 500,000 2.46
Landfill Sincan 5.6 44.8 91 125,000 2.79
Wind b Zeytineli 50 149 34 89,000 0.60
Diversion Sayan 14.9 48.3 37 26,550 0.55
type hydro
Storage Karasu 5.9 38.9 75 17,918 0.46
type hydro
a ITC, http://www.itcturkiye.com/, 2012.
b Futurecamp, http://fc-tk.futurecamp.de/, 2012.
2.5 CONCLUSIONS
This study focuses on the energy aspect of WWTPs. The use of the existing biogas
and hydropower energy potential in WWTPs has been analyzed. The new energy
laws and the market conditions in most countries around the world create an oppor-
tunity to harness this potential. As a case study, Tatlar WWTP in Ankara has been
investigated in a detailed manner. The annual electricity consumption of Tatlar
WWTP was 26.5 GWh in 2013. The installation of an Archimedean screw at the
outlet of the WWTP has a payback period of less than 3 years, and hydroelectricity
generation exceeds the electricity consumption by about 30%, producing clean and
feasible energy. The findings of the case study demonstrated that by using biogas
and hydro energy together, the energy recovery efficiency of a WWTP can exceed
100%, which is consistent with the operational data of Samra WWTP in Jordan.
These energy-related technological solutions can make considerable contributions to
sustainable WWTP development.
REFERENCES
Ak, M., Kentel, E., and Kucukali, S., 2016 A fuzzy logic tool to evaluate low-head hydropower
technologies at the outlet of wastewater treatment plants, Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews, 68, 727–737.
Al Seadi, T., Rutz, D., Prassl, H., Köttner, M., Finsterwalder, T., Volk, S., and Janssen, R.,
2008. Biogas Handbook, Published by University of Southern Denmark Esbjerg, Niels
Bohrs Vej, 9–10, ISBN 978-87-992962-0-0, pp. 21–29.
Appels, L., Baeyens, J., Degrève, J., and Dewil, R., 2008. Principles and potential of the
anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Progress in Energy and Combustion
Science, 34, 755–781.
Bachmann, N., 2009. Vorteile und Grenzen der Vergarung von leicht abbaubaren Industrie-
und Lebesmittelabfallen in Abwasserrinigungsanlagen. Federal Office of Energy,
Switzerland, No.290101/102963.