Page 86 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 86
Life Cycle Assessment of Beneficial Reuse of Waste Streams 67
Municipal Bar Grit Primary Secondary Treated water
Wastewater screens removal clarifier Aeration clarifier Disinfection discharge
Sludge
ww
Algae Algae Sludge
Dewatering
cultivation thickening Centrate
Water
Algae Sludge
Supernatant
Algae Lipid Anaerobic Digestate
Homogenization Dewatering
extraction digestion
Biooil Residual Biogas
Chemicals GHG emissions
Transesterification NG boiler
Elec.
Crude glycerol and heat
Biodiesel Electricity Land nutrients
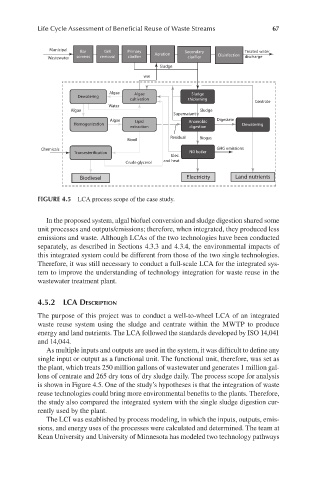
FIGURE 4.5 LCA process scope of the case study.
In the proposed system, algal biofuel conversion and sludge digestion shared some
unit processes and outputs/emissions; therefore, when integrated, they produced less
emissions and waste. Although LCAs of the two technologies have been conducted
separately, as described in Sections 4.3.3 and 4.3.4, the environmental impacts of
this integrated system could be different from those of the two single technologies.
Therefore, it was still necessary to conduct a full-scale LCA for the integrated sys-
tem to improve the understanding of technology integration for waste reuse in the
wastewater treatment plant.
4.5.2 lca DescripTion
The purpose of this project was to conduct a well-to-wheel LCA of an integrated
waste reuse system using the sludge and centrate within the MWTP to produce
energy and land nutrients. The LCA followed the standards developed by ISO 14,041
and 14,044.
As multiple inputs and outputs are used in the system, it was difficult to define any
single input or output as a functional unit. The functional unit, therefore, was set as
the plant, which treats 250 million gallons of wastewater and generates 1 million gal-
lons of centrate and 265 dry tons of dry sludge daily. The process scope for analysis
is shown in Figure 4.5. One of the study’s hypotheses is that the integration of waste
reuse technologies could bring more environmental benefits to the plants. Therefore,
the study also compared the integrated system with the single sludge digestion cur-
rently used by the plant.
The LCI was established by process modeling, in which the inputs, outputs, emis-
sions, and energy uses of the processes were calculated and determined. The team at
Kean University and University of Minnesota has modeled two technology pathways