Page 266 -
P. 266
10.12 CHAPTER TEN
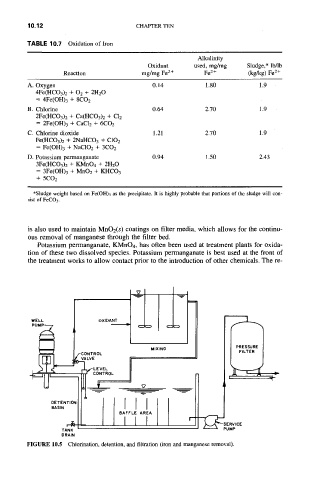
TABLE 10.7 Oxidation of Iron
Alkalinity
Oxidant used, mg/mg Sludge,* lb/lb
Reaction mg/mg Fe 2+ Fe 2+ (kg/kg) Fe 2+
A. Oxygen 0.14 1.80 1.9
4Fe(HCO3)2 + 02 + 2H20
= 4Fe(OH)3 + 8CO2
B. Chlorine 0.64 2.70 1.9
2Fe(HCO3)2 + Ca(HCO3)2 + C12
= 2Fe(OH)3 + CaC12 + 6CO2
C. Chlorine dioxide 1.21 2.70 1.9
Fe(HCO3)2 + 2NaHCO3 + C102
= Fe(OH)3 + NaC102 + 3CO2
D. Potassium permanganate 0.94 1.50 2.43
3Fe(HCO3)2 + KMnO4 + 2H20
= 3Fe(OH)3 + MnO2 + KHCO3
+ 5CO2
*Sludge weight based on Fe(OH)3 as the precipitate. It is highly probable that portions of the sludge will con-
sist of FeCO3.
is also used to maintain MnO2(s) coatings on filter media, which allows for the continu-
ous removal of manganese through the filter bed.
Potassium permanganate, KMnO4, has often been used at treatment plants for oxida-
tion of these two dissolved species. Potassium permanganate is best used at the front of
the treatment works to allow contact prior to the introduction of other chemicals. The re-
OXANT I
MIXING
,,,,, °L =
V
TANK UMP
DRAIN
FIGURE 10.5 Chlorination, detention, and filtration (iron and manganese removal).