Page 268 -
P. 268
10.14 CHAPTER TEN
~
80
0°C
0 60
-I-
~ 4o
20
6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5
pH
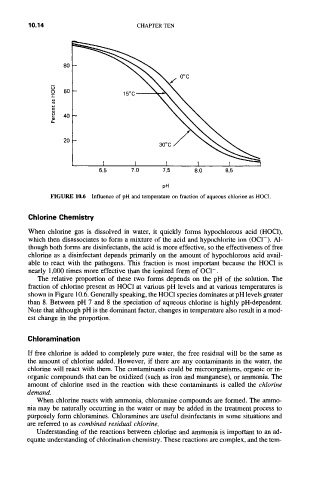
FIGURE 10.6 Influence of pH and temperature on fraction of aqueous chlorine as HOC1.
Chlorine Chemistry
When chlorine gas is dissolved in water, it quickly forms hypochlorous acid (HOC1),
which then disassociates to form a mixture of the acid and hypochlorite ion (OCI-). Al-
though both forms are disinfectants, the acid is more effective, so the effectiveness of free
chlorine as a disinfectant depends primarily on the amount of hypochlorous acid avail-
able to react with the pathogens. This fraction is most important because the HOC1 is
nearly 1,000 times more effective than the ionized form of OCI-.
The relative proportion of these two forms depends on the pH of the solution. The
fraction of chlorine present as HOCI at various pH levels and at various temperatures is
shown in Figure 10.6. Generally speaking, the HOCI species dominates at pH levels greater
than 8. Between pH 7 and 8 the speciation of aqueous chlorine is highly pH-dependent.
Note that although pH is the dominant factor, changes in temperature also result in a mod-
est change in the proportion.
Chloramination
If free chlorine is added to completely pure water, the free residual will be the same as
the amount of chlorine added. However, if there are any contaminants in the water, the
chlorine will react with them. The contaminants could be microorganisms, organic or in-
organic compounds that can be oxidized (such as iron and manganese), or ammonia. The
amount of chlorine used in the reaction with these contaminants is called the chlorine
demand.
When chlorine reacts with ammonia, chloramine compounds are formed. The ammo-
nia may be naturally occurring in the water or may be added in the treatment process to
purposely form chloramines. Chloramines are useful disinfectants in some situations and
are referred to as combined residual chlorine.
Understanding of the reactions between chlorine and ammonia is important to an ad-
equate understanding of chlorination chemistry. These reactions are complex, and the tem-