Page 506 -
P. 506
CHEMICALS AND CHEMICAL HANDLING 15.15
260
I 1
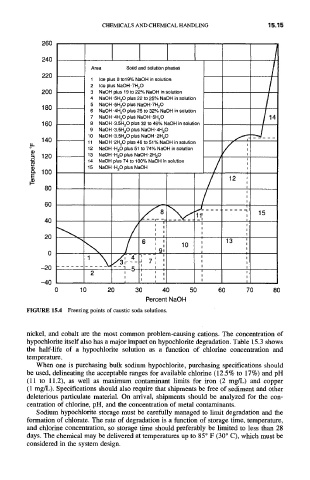
Area Solid and solution phases
220
1 Ice plus 0 to19% NaOH in solution
2 Ice plus NaOH.7H20
200 3 NaOH plus 19 to 22% NaOH in solution
4 NaOH,5H20 plus 22 to 25% NaOH in solution
5 NaOH.5H20 plus NaOH.7H20
180
6 NaOH,4H20 plus 25 to 32% NaOH in solution
7 NaOH-4H20 plus NaOH'5H20
1 60 8 NaOH.3.5H20 plus 32 to 46% NaOH in solution
9 NaOH-3.5H20 plus NaOH.4H20
10 NaOH.3.5H20 plus NaOH.2H20
140 11 NaOH.2H20 plus 46 to 51% NaOH in solution
12 NaOH.H20 plus 51 to 74% NaOH in solution
I
120 13 NaOH.H20 plus NaOH'2H20 #
I
14 NaOH plus 74 to 100% NaOH in solution
I
(1) 15 NaOH'H20 plus NaOH
I
100
I
E
/ 12
,
I
I
80
I
I
I
60 - /
t
..... ~ 15
, , I
I
-~
40
I
1
I
20 ,
13 I
lO ',
I
I
o ,,
I
71', ,
I
I
I
. . . . . . . . I I
-20 2 ' ' 1
I
I
I I
I I
I
-40 ~ '
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Percent NaOH
FIGURE 15.4 Freezing points of caustic soda solutions.
nickel, and cobalt are the most common problem-causing cations. The concentration of
hypochlorite itself also has a major impact on hypochlorite degradation. Table 15.3 shows
the half-life of a hypochlorite solution as a function of chlorine concentration and
temperature.
When one is purchasing bulk sodium hypochlorite, purchasing specifications should
be used, delineating the acceptable ranges for available chlorine (12.5% to 17%) and pH
(11 to 11.2), as well as maximum contaminant limits for iron (2 mg/L) and copper
(1 mg/L). Specifications should also require that shipments be free of sediment and other
deleterious particulate material. On arrival, shipments should be analyzed for the con-
centration of chlorine, pH, and the concentration of metal contaminants.
Sodium hypochlorite storage must be carefully managed to limit degradation and the
formation of chlorate. The rate of degradation is a function of storage time, temperature,
and chlorine concentration, so storage time should preferably be limited to less than 28
days. The chemical may be delivered at temperatures up to 85 ° F (30 ° C), which must be
considered in the system design.