Page 103 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 103
92 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
As found by Cox and Dadkhah (1995), the orientation averaging model with simple
corrections for tow waviness can provide an excellent prediction of the in-plane
macroscopic elastic constants and a fair estimation for elastic constants related to
through-thickness strains.
4.4.2 Mixed Iso-Stress and Iso-Strain Models
Tan et al. (1998, 1999a,b) proposed a mixed iso-stress and iso-strain based unit cell
modelling scheme for predicting mechanical and thermo-elastic properties for 3D
orthogonal and angle-interlock composite materials. The modelling scheme was
experimentally validated by comparing the measured elastic properties of 3D orthogonal
carbon fibre reinforced composites and 3D glass fibre reinforced composites with those
predicted (Tan et al., 2000b, 2001). In the following, we will describe the fundamentals
of the mixed iso-stress and iso-strain unit cell modelling scheme by considering a 3D
orthogonal woven composite material.
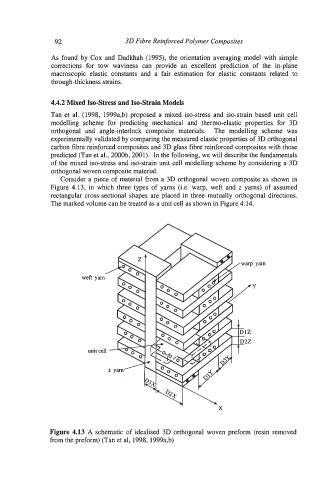
Consider a piece of material from a 3D orthogonal woven composite as shown in
Figure 4.13, in which three types of yarns (Le. warp, weft and z yarns) of assumed
rectangular cross-sectional shapes are placed in three mutually orthogonal directions.
The marked volume can be treated as a unit cell as shown in Figure 4.14.
I
weft yarn
unit cell
X
Figure 4.13 A schematic of idealised 3D orthogonal woven preform (resin removed
from the preform) (Tan et al, 1998, 1999a,b)