Page 151 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 151
140 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
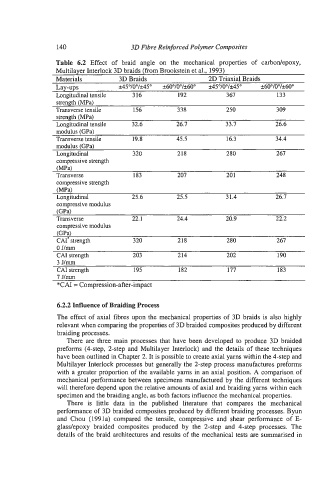
Table 6.2 Effect of braid angle on the mechanical properties of carbodepoxy,
Multilayer Interlock 3D braids (from Brookstein et al., 1993)
Materials 3D Braids 2D Triaxial Braids
Lay-ups ~k45~lO~l~45" ~60°10Q/k60" ~45"10"1~k45~ k60"/O01*60"
Longitudinal tensile 316 192 3 67 133
strength (MPa)
Transverse tensile 156 338 250 309
strength (MPa)
Longitudinal tensile 32.6 26.7 33.7 26.6
modulus (GPa)
Transverse tensile 19.8 45.5 16.3 34.4
modulus (GPa)
Longitudinal 320 218 280 267
compressive strength
(MPa)
Transverse 183 207 201 248
compressive strength
-
(MPa)
Longitudinal 25.6 25.5 31.4 26.7
compressive modulus
(GPa)
Transverse 22.1 24.4 20.9 22.2
compressive modulus
(GPa)
CAI' strength 320 218 280 267
0 J/mm
CAI strength 203 214 202 190
3 Jlmm
CAI strength - 195 182 177 183
7 J/mm
*CAI = Compression-after-impact
6.2.2 Influence of Braiding Process
The effect of axial fibres upon the mechanical properties of 3D braids is also highly
relevant when comparing the properties of 3D braided composites produced by different
braiding processes.
There are three main processes that have been developed to produce 3D braided
preforms (Cstep, 2-step and Multilayer Interlock) and the details of these techniques
have been outlined in Chapter 2. It is possible to create axial yarns within the 4-step and
Multilayer Interlock processes but generally the 2-step process manufactures preforms
with a greater proportion of the available yams in an axial position. A comparison of
mechanical performance between specimens manufactured by the different techniques
will therefore depend upon the relative amounts of axial and braiding yarns within each
specimen and the braiding angle, as both factors influence the mechanical properties.
There is little data in the published literature that compares the mechanical
performance of 3D braided composites produced by different braiding processes. B yun
and Chou (1991a) compared the tensile, compressive and shear performance of E-
glass/epoxy braided composites produced by the 2-step and 4-step processes. The
details of the braid architectures and results of the mechanical tests are summarised in