Page 161 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 161
150 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
Huysmans et al. (1996), both of whom investigated the properties of various warp knit
architectures. Tables 7.1 and 7.2 summarise these results. In both sets of results it can
be clearly seen that not only can the knitting process produce reinforcement fabrics with
a broad range of properties but that a variation in a knit architecture can change a fabric
from one with approximately isotropic properties to one with strongly anisotropic
behaviour. In a similar fashion to woven fabrics, both the stiffness and strength of
knitted composites can be improved not only by increased fibre volume fraction, but
also by preferential fibre orientations within the fabric. This is illustrated in Figure 7.5,
which shows the knit architectures of single dembigh, 1x3 single cord and 1x4 single
cord that were examined by Wu et al. (1993). As the proportion of fibres orientated in
the course direction increases so to does the tensile performance of the composite
material in the course direction whilst the wale direction performance remains relatively
unchanged. It should be noted that this preferential orientation of the fibres can also
lead to the directional properties of knitted composites being far superior to that of
random mats although still less than typical 2D woven fabrics.
h 1;
z 140 -
5 120 -
+ Ramakrishna et all997
2 100 -
t; W Huang et al2001
o 80 - 0
e A Hohfeld et al 1994
.d
$ 60- €
H 0 Hohfeld et a1 1994
40 -
0 Mat
20 -
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Fibre Volume Fraction (%)
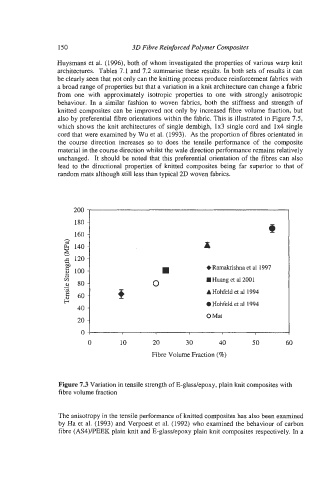
Figure 7.3 Variation in tensile strength of E-glass/epoxy, plain knit composites with
fibre volume fraction
The anisotropy in the tensile performance of knitted composites has also been examined
by Ha et al. (1993) and Verpoest et al. (1992) who examined the behaviour of carbon
fibre (AS4)PEEK plain knit and E-glass/epoxy plain knit composites respectively. In a