Page 166 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 166
Knitted Composite Materials 155
al., 1998; Leong et al., 1999; and Khondker et al., 2001a) have reported that for 1x1 rib
and milano weft knitted composite materials, the compressive strength is significantly
better than the tensile strength whilst the compressive modulus is similar to, or slightly
less than, the tensile modulus. Examples of this behaviour are given in Table 7.4. Again
distinctly different from the tension properties;the effect of changing loop lengths and
stitch densities upon the compressive properties is far less significant. Khondker et al
2001b reported that in E-glasshnyl ester weft knitted composites (plain, rib and milano
architectures) at best only marginal improvement was observed in the compression
strength with an increase in loop length whilst negligible effect was observed on the
compressive modulus.
\ I I I
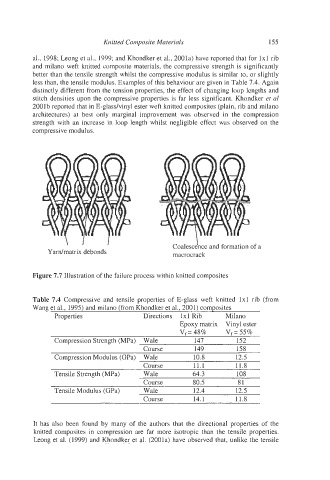
Yardmatrix debonds Coalescence and formation of a
macrocrac k
Figure 7.7 Illustration of the failure process within knitted composites
Table 7.4 Compressive and tensile properties of E-glass weft knitted 1x1 rib (from
Wang et al., 1995) and milano (from Khondker et al., 2001) composites
Properties Directions 1x1 Rib Milano
Epoxy matrix Vinyl ester
Vf = 48% Vf = 55%
Compression Strength (MPa) Wale 147 152
Course 149 158
Compression Modulus (GPa) Wale 10.8 12.5
Course 11.1 11.8
Tensile Strength (ma) Wale 64.3 108
Course 80.5 81
Tensile Modulus (GPa) Wale 12.4 12.5
Course 14.1 11.8
It has also been found by many of the authors that the directional properties of the
knitted composites in compression are far more isotropic than the tensile properties.
Leong et al. (1999) and Khondker et al. (2001a) have observed that, unlike the tensile