Page 168 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 168
Knitted Composite Materials 157
of non-crimps over conventional knitted composites through the inclusion of straight,
inlayed yarns is however achieved at the cost of the high formability of the conventional
knitted fabric.
The use of non-crimp fabrics is now commonplace within the maritime industry and
in the manufacture of wind turbine blades and, as pointed out in Chapter 2, it is a prime
material candidate for future aircraft programs. There has been a great deal of
development of this fabric style, with improvements in the visual quality of the fabric
and the range of lay up options available as well as improvements in its mechanical
performance.
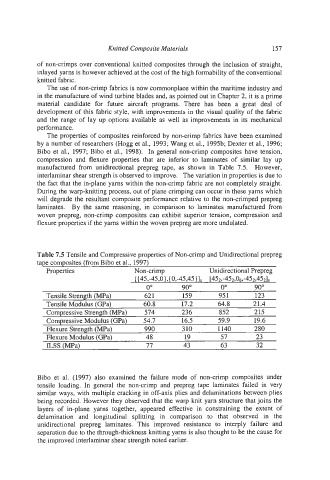
The properties of composites reinforced by non-crimp fabrics have been examined
by a number of researchers (Hogg et al., 1993; Wang et al., 1995b; Dexter et al., 1996;
Bib0 et al., 1997; Bib0 et al., 1998). In general non-crimp composites have tension,
compression and flexure properties that are inferior to laminates of similar lay up
manufactured from unidirectional prepreg tape, as shown in Table 7.5. However,
interlaminar shear strength is observed to improve. The variation in properties is due to
the fact that the in-plane yarns within the non-crimp fabric are not completely straight.
During the warp-knitting process, out of plane crimping can occur in these yarns which
will degrade the resultant composite performance relative to the non-crimped prepreg
laminates. By the same reasoning, in comparison to laminates manufactured from
woven prepreg, non-crimp composites can exhibit superior tension, compression and
flexure properties if the yarns within the woven prepreg are more undulated.
Table 7.5 Tensile and Compressive properties of Non-crimp and Unidirectional prepreg
tape composites (from Bib0 et al., 1997)
Properties Non-crimp Unidirectional Prepreg
[ [45,-45,0),{ 09-45945 11s [452,-452,06,-452,4521s
0" 90" 0" 90"
Tensile Strength (ma) 62 1 159 95 1 123
Tensile Modulus (GPa) 60.8 17.2 64.8 21.4
Compressive Strength (ma) 574 236 852 215
Compressive Modulus (GPa) 54.7 16.5 59.9 19.6
Flexure Strength (ma) 990 310 I140 280
Flexure Modulus (GPa) 48 19 57 23
ILSS (ma) 77 43 63 32
Bib0 et al. (1997) also examined the failure mode of non-crimp composites under
tensile loading. In general the non-crimp and prepreg tape laminates failed in very
similar ways, with multiple cracking in off-axis plies and delaminations between plies
being recorded. However they observed that the warp knit yarn structure that joins the
layers of in-plane yarns together, appeared effective in constraining the extent of
delamination and longitudinal splitting in comparison to that observed in the
unidirectional prepreg laminates. This improved resistance to interply failure and
separation due to the through-thickness knitting yarns is also thought to be the cause for
the improved interlaminar shear strength noted earlier.