Page 171 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 171
160 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
Within each of the knit architectures the authors also examined the effect of varying the
stitch density upon the composite impact performance. No significant effect on the
impact resistance was seen within any of the three architectures even though the stitch
density changes by a factor of two for each material. This lack of any conclusive change
with stitch density was also observed for the impact tolerance of the knitted composites.
This result is possibly expected as the undamaged compressive properties of knitted
composites showed very little effect from variations in the loop parameters within any
of the knit architectures examined. This was attributed to the dominant influence the
matrix plays in the compressive properties, therefore given a similar extent of damage
created within the composite, the remaining compressive strength should also be
similar.
The behaviour of knitted composites under impact conditions is clearly a complex
situation but what is worth emphasising is the ability of knitted composites to absorb
large amounts of impact energy relative to other reinforcement forms and to suffer less
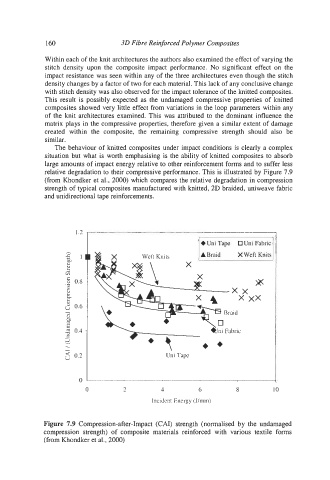
relative degradation to their compressive performance. This is illustrated by Figure 7.9
(from Khondker et al., 2000) which compares the relative degradation in compression
strength of typical composites manufactured with knitted, 2D braided, uniweave fabric
and unidirectional tape reinforcements.
1.2
1 Uni Tape 0 Uni Fabric
h X Weft Knits
5 1
M
c
E
cn
Y
._ 0.8
v1
I/i
E
E
6 0.6
B
3
E
2 0.4
.
c
2
3
5 0.2 Uni Tape
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
Incident Energy (J/mm)
Figure 7.9 Compression-after-Impact (CAI) strength (normalised by the undamaged
compression strength) of composite materials reinforced with various textile forms
(from Khondker et al., 2000)