Page 189 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 189
178 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
The mechanism responsible for the slight reduction to the interlaminar shear strength of
stitched composites is not fully understood. Some studies have observed that pure
interlaminar shear cracking along the mid-plane of stitched composites does not always
occur. Instead, failure occurs by cracking of the most highly distorted fibres close to the
stitches rather than by pure interlaminar shear cracking. It is proposed that this change
to the failure mechanism from pure shear cracking to fibre cracking is the likely cause
for the lower interlaminar shear strength of some stitched composites (Mouritz et al.,
1996).
8.3.4 Creep Properties of Stitched Composites
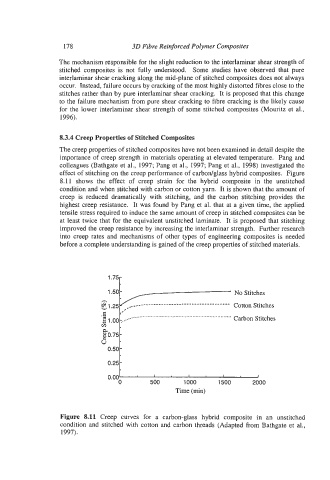
The creep properties of stitched composites have not been examined in detail despite the
importance of creep strength in materials operating at elevated temperature. Pang and
colleagues (Bathgate et al., 1997; Pang et al., 1997; Pang et al., 1998) investigated the
effect of stitching on the creep performance of carbodglass hybrid composites. Figure
8.11 shows the effect of creep strain for the hybrid composite in the unstitched
condition and when stitched with carbon or cotton yarn. It is shown that the amount of
creep is reduced dramatically with stitching, and the carbon stitching provides the
highest creep resistance. It was found by Pang et a]. that at a given time, the applied
tensile stress required to induce the same amount of creep in stitched composites can be
at least twice that for the equivalent unstitched laminate. It is proposed that stitching
improved the creep resistance by increasing the interlaminar strength. Further research
into creep rates and mechanisms of other types of engineering composites is needed
before a complete understanding is gained of the creep properties of stitched materials.
1.75-
No Stitches
___________-------_-________________
Cotton Stitches
c I'
s 1 .oo :..."'
I- ................................................................ Carbon Stitches
m
::::I . , , , , , . ,
0.00
0 500 1000 1500 2000
Time (min)
Figure 8.11 Creep curves for a carbon-glass hybrid composite in an unstitched
condition and stitched with cotton and carbon threads (Adapted from Bathgate et al.,
1997).