Page 196 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 196
Stitched Composites 185
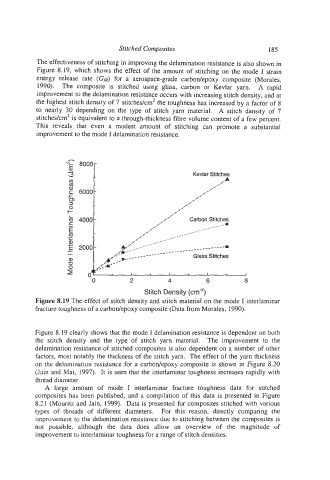
The effectiveness of stitching in improving the delamination resistance is also shown in
Figure 8.19, which shows the effect of the amount of stitching on the mode I strain
energy release rate (GI#) for a aerospace-grade carbodepoxy composite (Morales,
1990). The composite is stitched using glass, carbon or Kevlar yarn. A rapid
improvement to the delamination resistance occurs with increasing stitch density, and at
the highest stitch density of 7 stitchedcm' the toughness has increased by a factor of 8
to nearly 30 depending on the type of stitch yarn material. A stitch density of 7
stitches/cm* is equivalent to a through-thickness fibre volume content of a few percent.
This reveals that even a modest amount of stitching can promote a substantial
improvement to the mode I delamination resistance.
-
"E 8000-
1
2 Kevlar Stitches
v) A
v) ).*. .*I
? 6000- <./'
2z
u) /.I'
3 /.I.
0 /.)*
f- ,'
5 4000- ,. I' 0- Carbon Stitches
.- //. ,.*- ..... /..-
E *...-. . . . .--.
_...
(d - / .,-.
z .* *,-I .... __..-
E
- 2000- &'. ....a I.-.. ____--------=
I ...-
-
,.<" -.
- /;I./ .-- - _______----*--
-
--
-
-
-
Glass Stitches
a,
-0 /+=
r" O'Y I I I I
Figure 8.19 clearly shows that the mode I delamination resistance is dependent on both
the stitch density and the type of stitch yarn material. The improvement to the
delamination resistance of stitched composites is also dependent on a number of other
factors, most notably the thickness of the stitch yam. The effect of the yarn thickness
on the delamination resistance for a carbodepoxy composite is shown in Figure 8.20
(Jain and Mai, 1997). It is seen that the interlaminar toughness increases rapidly with
thread diameter.
A large amount of mode I interlaminar fracture toughness data for stitched
composites has been published, and a compilation of this data is presented in Figure
8.21 (Mouritz and Jain, 1999). Data is presented for composites stitched with various
types of threads of different diameters. For this reason, directly comparing the
improvement to the delamination resistance due to stitching between the composites is
not possible, although the data does allow an overview of the magnitude of
improvement to interlaminar toughness for a range of stitch densities.