Page 223 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 223
212 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
these materials are highly resistant to interlaminar cracking and through-thickness
failure. Z-fibersTM are highly effective in improving the mode I interlaminar fracture
toughness (GI,) of tape laminates (Freitas et al., 1994; Cartit and Partridge, 1999a,
1999b; Orafticaux et al., 2000; Partridge and Carti6,2001). This is shown in Figure 9.9
that shows the effect of Z-fiberTM content on the delamination resistance of a
carbodepoxy laminate. The mode I interlaminar fracture toughness is seen to increase
rapidly with the amount of Z-fibersm. The maximum GI, value of 11.6 kJ/m2 was
achieved with the relatively modest 2-fiberTM content of 1.5%, and this level of
interlaminar toughness is similar or greater than that achieved by 3D weaving, braiding,
knitting or stitching. Carti6 and Partridge (1999b) found that the level of interlaminar
toughening is also dependent on the diameter of the z-pins, with thinner pins providing
higher delamination resistance. For example, it was found that the mode I interlaminar
toughness of a carbordepoxy tape laminate reinforced with 2% Z-fibersm was more
than doubled when the pin diameter was reduced from 0.50 mm to 0.28 mm.
Measured Data
!
Theoretical Predictio r/
v
0 5 10 15 20
Initial Fibre Waviness (degrees)
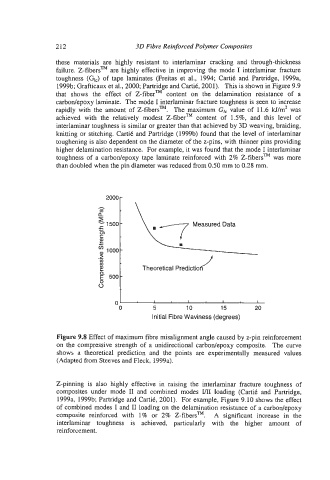
Figure 9.8 Effect of maximum fibre misalignment angle caused by z-pin reinforcement
on the compressive strength of a unidirectional carbodepoxy composite. The curve
shows a theoretical prediction and the points are experimentally measured values
(Adapted from Steeves and Fleck, 1999a).
2-pinning is also highly effective in raising the interlaminar fracture toughness of
composites under mode I1 and combined modes HI loading (CartiC and Partridge,
1999a, 1999b; Partridge and Carti&, 2001). For example, Figure 9.10 shows the effect
of combined modes I and I1 loading on the delamination resistance of a carbodepoxy
composite reinforced with 1% or 2% 2-fibersTM. A significant increase in the
interlaminar toughness is achieved, particularly with the higher amount of
reinforcement.