Page 155 -
P. 155
5 - PROJECT SCOPE MANAGEMENT
1.0
Value Management
System Project
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4
Needs Standards Systems Project
Assessment Development Engineering Management
5
1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4
Current System Requirements Alternatives System Requirements
Audit Determination Development Development
1.1.1.1 1.1.2.1 1.1.3.1
Components Gap Alternatives
Identification Assessment Identification
1.1.1.2 1.1.2.2 1.1.3.2
Components Requirements Alternatives
Analysis Changes Identification Analysis
The WBS is illustrative only. It is not intended to represent the full project scope of any specific project,
nor to imply that this is the only way to organize a WBS on this type of project.
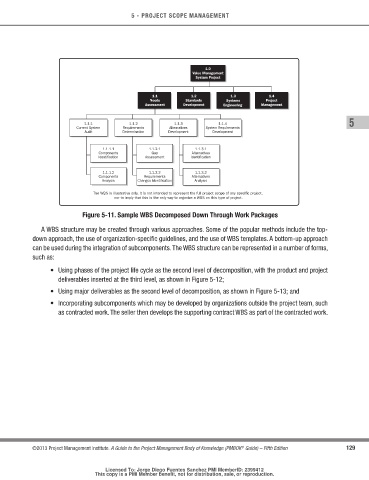
Figure 5-11. Sample WBS decomposed down through Work Packages
A WBS structure may be created through various approaches. Some of the popular methods include the top-
down approach, the use of organization-specific guidelines, and the use of WBS templates. A bottom-up approach
can be used during the integration of subcomponents. The WBS structure can be represented in a number of forms,
such as:
• Using phases of the project life cycle as the second level of decomposition, with the product and project
deliverables inserted at the third level, as shown in Figure 5-12;
• Using major deliverables as the second level of decomposition, as shown in Figure 5-13; and
• Incorporating subcomponents which may be developed by organizations outside the project team, such
as contracted work. The seller then develops the supporting contract WBS as part of the contracted work.
®
©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition 129
Licensed To: Jorge Diego Fuentes Sanchez PMI MemberID: 2399412
This copy is a PMI Member benefit, not for distribution, sale, or reproduction.