Page 343 -
P. 343
11 - PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
• risk categories. Provide a means for grouping potential causes of risk. Several approaches can be
used, for example, a structure based on project objectives by category. A risk breakdown structure (RBS)
helps the project team to look at many sources from which project risk may arise in a risk identification
exercise. Different RBS structures will be appropriate for different types of projects. An organization can
use a previously prepared custom categorization framework, which may take the form of a simple list of
categories or may be structured into an RBS. The RBS is a hierarchical representation of risks according
to their risk categories. An example is shown in Figure 11-4.
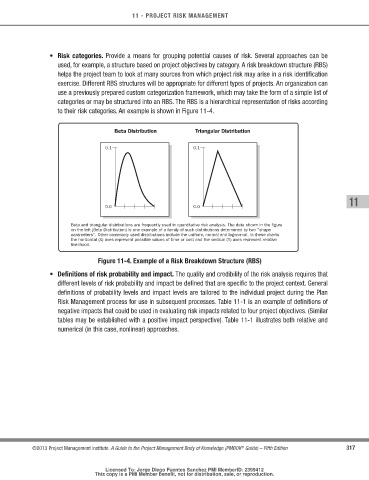
Beta Distribution Triangular Distribution
0.1 0.1
11
0.0 0.0
Beta and triangular distributions are frequently used in quantitative risk analysis. The data shown in the figure
on the left (Beta Distribution) is one example of a family of such distributions determined by two "shape
parameters". Other commonly used distributions include the uniform, normal and lognormal. In these charts
the horizontal (X) axes represent possible values of time or cost and the vertical (Y) axes represent relative
likelihood.
Figure 11-4. Example of a risk Breakdown Structure (rBS)
• definitions of risk probability and impact. The quality and credibility of the risk analysis requires that
different levels of risk probability and impact be defined that are specific to the project context. General
definitions of probability levels and impact levels are tailored to the individual project during the Plan
Risk Management process for use in subsequent processes. Table 11-1 is an example of definitions of
negative impacts that could be used in evaluating risk impacts related to four project objectives. (Similar
tables may be established with a positive impact perspective). Table 11-1 illustrates both relative and
numerical (in this case, nonlinear) approaches.
®
©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition 317
Licensed To: Jorge Diego Fuentes Sanchez PMI MemberID: 2399412
This copy is a PMI Member benefit, not for distribution, sale, or reproduction.