Page 344 -
P. 344
11 - PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
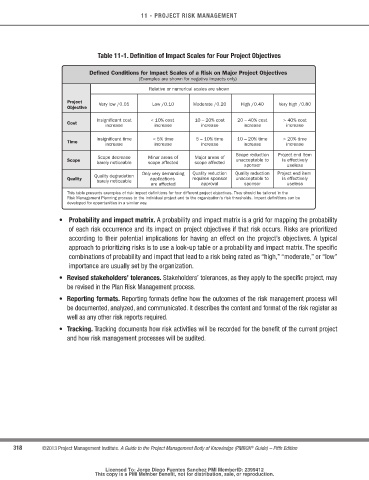
table 11-1. definition of Impact Scales for Four Project objectives
Defined Conditions for Impact Scales of a Risk on Major Project Objectives
(Examples are shown for negative impacts only)
Relative or numerical scales are shown
Project Very low /0.05 Low /0.10 Moderate /0.20 High /0.40 Very high /0.80
Objective
Insignificant cost < 10% cost 10 – 20% cost 20 – 40% cost > 40% cost
Cost
increase increase increase increase increase
Insignificant time < 5% time 5 – 10% time 10 – 20% time > 20% time
Time increase increase increase increase increase
Scope reduction Project end item
Scope decrease Minor areas of Major areas of
Scope barely noticeable scope affected scope affected unacceptable to is effectively
sponsor useless
Only very demanding Quality reduction Quality reduction Project end item
Quality degradation
Quality applications requires sponsor unacceptable to is effectively
barely noticeable
are affected approval sponsor useless
This table presents examples of risk impact definitions for four different project objectives. They should be tailored in the
Risk Management Planning process to the individual project and to the organization's risk thresholds. Impact definitions can be
developed for opportunities in a similar way.
• Probability and impact matrix. A probability and impact matrix is a grid for mapping the probability
of each risk occurrence and its impact on project objectives if that risk occurs. Risks are prioritized
according to their potential implications for having an effect on the project’s objectives. A typical
approach to prioritizing risks is to use a look-up table or a probability and impact matrix. The specific
combinations of probability and impact that lead to a risk being rated as “high,” “moderate,” or “low”
importance are usually set by the organization.
• revised stakeholders’ tolerances. Stakeholders’ tolerances, as they apply to the specific project, may
be revised in the Plan Risk Management process.
• reporting formats. Reporting formats define how the outcomes of the risk management process will
be documented, analyzed, and communicated. It describes the content and format of the risk register as
well as any other risk reports required.
• tracking. Tracking documents how risk activities will be recorded for the benefit of the current project
and how risk management processes will be audited.
318 ©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition
®
Licensed To: Jorge Diego Fuentes Sanchez PMI MemberID: 2399412
This copy is a PMI Member benefit, not for distribution, sale, or reproduction.