Page 16 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 16
8 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
5
4
Adsorption (mg Base/g clay) 3 2 pH8
pH5
1
0
0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000 30000
Salinity (ppm)
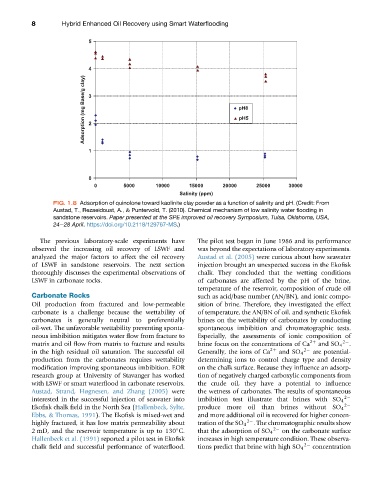
FIG. 1.8 Adsorption of quinolone toward kaolinite clay powder as a function of salinity and pH. (Credit: From
Austad, T., Rezaeidoust, A., & Puntervold, T. (2010). Chemical mechanism of low salinity water flooding in
sandstone reservoirs. Paper presented at the SPE improved oil recovery Symposium, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA,
24e28 April. https://doi.org/10.2118/129767-MS.)
The previous laboratory-scale experiments have The pilot test began in June 1986 and its performance
observed the increasing oil recovery of LSWF and was beyond the expectations of laboratory experiments.
analyzed the major factors to affect the oil recovery Austad et al. (2005) were curious about how seawater
of LSWF in sandstone reservoirs. The next section injection brought an unexpected success in the Ekofisk
thoroughly discusses the experimental observations of chalk. They concluded that the wetting conditions
LSWF in carbonate rocks. of carbonates are affected by the pH of the brine,
temperature of the reservoir, composition of crude oil
Carbonate Rocks such as acid/base number (AN/BN), and ionic compo-
Oil production from fractured and low-permeable sition of brine. Therefore, they investigated the effect
carbonate is a challenge because the wettability of of temperature, the AN/BN of oil, and synthetic Ekofisk
carbonates is generally neutral to preferentially brines on the wettability of carbonates by conducting
oil-wet. The unfavorable wettability preventing sponta- spontaneous imbibition and chromatographic tests.
neous imbibition mitigates water flow from fracture to Especially, the assessments of ionic composition of
matrix and oil flow from matrix to fracture and results brine focus on the concentrations of Ca 2þ and SO 4 2 .
in the high residual oil saturation. The successful oil Generally, the ions of Ca 2þ and SO 4 2 are potential-
production from the carbonates requires wettability determining ions to control charge type and density
modification improving spontaneous imbibition. EOR on the chalk surface. Because they influence an adsorp-
research group at University of Stavanger has worked tion of negatively charged carboxylic components from
with LSWF or smart waterflood in carbonate reservoirs. the crude oil, they have a potential to influence
Austad, Strand, Høgnesen, and Zhang (2005) were the wetness of carbonates. The results of spontaneous
interested in the successful injection of seawater into imbibition test illustrate that brines with SO 4 2
Ekofisk chalk field in the North Sea (Hallenbeck, Sylte, produce more oil than brines without SO 4 2
Ebbs, & Thomas, 1991). The Ekofisk is mixed-wet and and more additional oil is recovered for higher concen-
highly fractured, it has low matrix permeability about tration of the SO 4 2 . The chromatographic results show
2 mD, and the reservoir temperature is up to 130 C. that the adsorption of SO 4 2 on the carbonate surface
Hallenbeck et al. (1991) reported a pilot test in Ekofisk increases in high temperature condition. These observa-
chalk field and successful performance of waterflood. tions predict that brine with high SO 4 2 concentration