Page 83 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 83
CHAPTER 4 Hybrid Chemical EOR Using Low-Salinity and Smart Waterflood 75
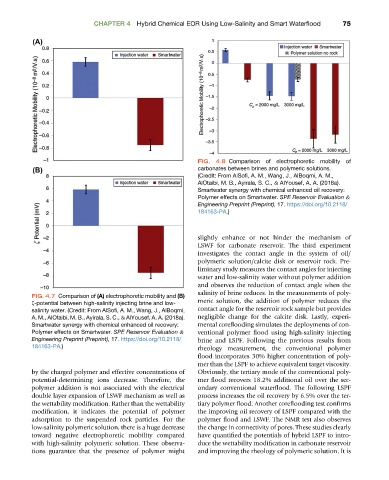
FIG. 4.8 Comparison of electrophoretic mobility of
carbonates between brines and polymeric solutions.
(Credit: From AlSofi, A. M., Wang, J., AlBoqmi, A. M.,
AlOtaibi, M. B., Ayirala, S. C., & AlYousef, A. A. (2018a).
Smartwater synergy with chemical enhanced oil recovery:
Polymer effects on Smartwater. SPE Reservoir Evaluation &
Engineering Preprint (Preprint), 17. https://doi.org/10.2118/
184163-PA.)
slightly enhance or not hinder the mechanism of
LSWF for carbonate reservoir. The third experiment
investigates the contact angle in the system of oil/
polymeric solution/calcite disk or reservoir rock. Pre-
liminary study measures the contact angles for injecting
water and low-salinity water without polymer addition
and observes the reduction of contact angle when the
FIG. 4.7 Comparison of (A) electrophoretic mobility and (B) salinity of brine reduces. In the measurements of poly-
z-potential between high-salinity injecting brine and low- meric solution, the addition of polymer reduces the
salinity water. (Credit: From AlSofi, A. M., Wang, J., AlBoqmi, contact angle for the reservoir rock sample but provides
A. M., AlOtaibi, M. B., Ayirala, S. C., & AlYousef, A. A. (2018a). negligible change for the calcite disk. Lastly, experi-
Smartwater synergy with chemical enhanced oil recovery: mental coreflooding simulates the deployments of con-
Polymer effects on Smartwater. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & ventional polymer flood using high-salinity injecting
Engineering Preprint (Preprint), 17. https://doi.org/10.2118/ brine and LSPF. Following the previous results from
184163-PA.) rheology measurement, the conventional polymer
flood incorporates 30% higher concentration of poly-
mer than the LSPF to achieve equivalent target viscosity.
by the charged polymer and effective concentrations of Obviously, the tertiary mode of the conventional poly-
potential-determining ions decrease. Therefore, the mer flood recovers 18.2% additional oil over the sec-
polymer addition is not associated with the electrical ondary conventional waterflood. The following LSPF
double layer expansion of LSWF mechanism as well as process increases the oil recovery by 6.5% over the ter-
the wettability modification. Rather than the wettability tiary polymer flood. Another coreflooding test confirms
modification, it indicates the potential of polymer the improving oil recovery of LSPF compared with the
adsorption to the suspended rock particles. For the polymer flood and LSWF. The NMR test also observes
low-salinity polymeric solution, there is a huge decrease the change in connectivity of pores. These studies clearly
toward negative electrophoretic mobility compared have quantified the potentials of hybrid LSPF to intro-
with high-salinity polymeric solution. These observa- duce the wettability modification in carbonate reservoir
tions guarantee that the presence of polymer might and improving the rheology of polymeric solution. It is