Page 87 - A Working Method Approach For Introductory Physical Chemistry Calculations
P. 87
Electrochemistry I: Galvanic Cells 71
4
reduction
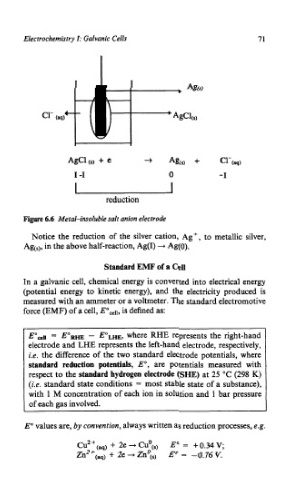
Figure 6.6 Metal-insoluble salt anion electrode
Notice the reduction of the silver cation, Agf, to metallic silver,
Age), in the above half-reaction, Ag(1) + Ag(0).
Standard EMF of a Cell
In a galvanic cell, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy
(potential energy to kinetic energy), and the electricity produced is
measured with an ammeter or a voltmeter. The standard electromotive
force (EMF) of a cell, Eocell, is defined as:
Eoceu = E"R~E - EoLHE, where RHE represents the right-hand
electrode and LHE represents the left-hand electrode, respectively,
i.e. the difference of the two standard electrode potentials, where
standard reduction potentials, E", are potentials measured with
respect to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) at 25 "C (298 K)
(i.e. standard state conditions = most stable state of a substance),
with 1 M concentration of each ion in solution and 1 bar pressure
of each gas involved.
E" values are, by convention, always written as reduction processes, e.g.
+
CU'+(~~) 2e + CU'(~) E" = + 0.34 V;
Znzf(,) + 2e + Zn'(,) E" = -0.76 V.