Page 116 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 116
CHAPT E R 2 Introduction to Transaction Processing 87
FI GUR E
2-39 VIRTUAL STORAGE ACCESS METHOD (VSAM) USED FOR DIRECT ACCESS
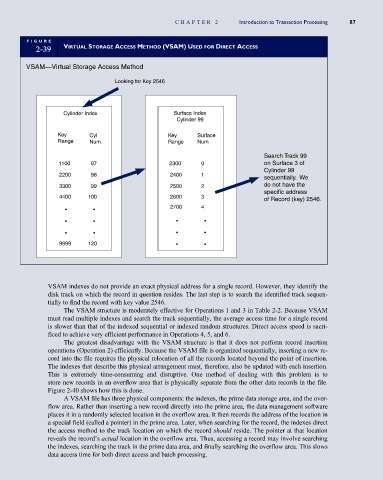
VSAM—Virtual Storage Access Method
Looking for Key 2546
Cylinder Index Surface Index
Cylinder 99
Key Cyl Key Surface
Range Num Range Num
Search Track 99
1100 97 2300 0 on Surface 3 of
Cylinder 99
2200 98 2400 1
sequentially. We
3300 99 2500 2 do not have the
specific address
4400 100 2600 3
of Record (key) 2546.
2700 4
9999 120
VSAM indexes do not provide an exact physical address for a single record. However, they identify the
disk track on which the record in question resides. The last step is to search the identified track sequen-
tially to find the record with key value 2546.
The VSAM structure is moderately effective for Operations 1 and 3 in Table 2-2. Because VSAM
must read multiple indexes and search the track sequentially, the average access time for a single record
is slower than that of the indexed sequential or indexed random structures. Direct access speed is sacri-
ficed to achieve very efficient performance in Operations 4, 5, and 6.
The greatest disadvantage with the VSAM structure is that it does not perform record insertion
operations (Operation 2) efficiently. Because the VSAM file is organized sequentially, inserting a new re-
cord into the file requires the physical relocation of all the records located beyond the point of insertion.
The indexes that describe this physical arrangement must, therefore, also be updated with each insertion.
This is extremely time-consuming and disruptive. One method of dealing with this problem is to
store new records in an overflow area that is physically separate from the other data records in the file.
Figure 2-40 shows how this is done.
A VSAM file has three physical components: the indexes, the prime data storage area, and the over-
flow area. Rather than inserting a new record directly into the prime area, the data management software
places it in a randomly selected location in the overflow area. It then records the address of the location in
a special field (called a pointer) in the prime area. Later, when searching for the record, the indexes direct
the access method to the track location on which the record should reside. The pointer at that location
reveals the record’s actual location in the overflow area. Thus, accessing a record may involve searching
the indexes, searching the track in the prime data area, and finally searching the overflow area. This slows
data access time for both direct access and batch processing.