Page 119 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 119
90 PART I Overview of Accounting Information Systems
FI GU RE
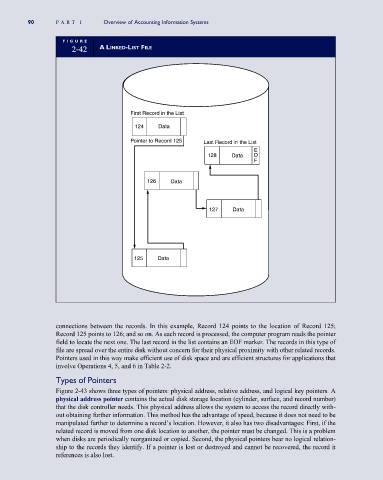
2-42 ALINKED-LIST FILE
First Record in the List
124 Data
Pointer to Record 125 Last Record in the List
E
128 Data O
F
126 Data
127 Data
125 Data
connections between the records. In this example, Record 124 points to the location of Record 125;
Record 125 points to 126; and so on. As each record is processed, the computer program reads the pointer
field to locate the next one. The last record in the list contains an EOF marker. The records in this type of
file are spread over the entire disk without concern for their physical proximity with other related records.
Pointers used in this way make efficient use of disk space and are efficient structures for applications that
involve Operations 4, 5, and 6 in Table 2-2.
Types of Pointers
Figure 2-43 shows three types of pointers: physical address, relative address, and logical key pointers. A
physical address pointer contains the actual disk storage location (cylinder, surface, and record number)
that the disk controller needs. This physical address allows the system to access the record directly with-
out obtaining further information. This method has the advantage of speed, because it does not need to be
manipulated further to determine a record’s location. However, it also has two disadvantages: First, if the
related record is moved from one disk location to another, the pointer must be changed. This is a problem
when disks are periodically reorganized or copied. Second, the physical pointers bear no logical relation-
ship to the records they identify. If a pointer is lost or destroyed and cannot be recovered, the record it
references is also lost.